SUMMARY CMI
BILTRICIDE®
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) summary
The full CMI on the next page has more details. If you are worried about using this medicine, speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
1. Why am I using BILTRICIDE?
BILTRICIDE contains the active ingredient praziquantel. BILTRICIDE is used for the treatment of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis, which is a chronic parasitic infestation in humans caused by blood flukes (worms).
For more information, see Section 1. Why am I using BILTRICIDE? in the full CMI.
2. What should I know before I use BILTRICIDE?
Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to BILTRICIDE or any of the ingredients listed at the end of the CMI.
Talk to your doctor if you have any other medical conditions, take any other medicines, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding.
For more information, see Section 2. What should I know before I use BILTRICIDE? in the full CMI.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Some medicines may interfere with BILTRICIDE and affect how it works.
A list of these medicines is in Section 3. What if I am taking other medicines? in the full CMI.
4. How do I use BILTRICIDE?
- You must take all the BILTRICIDE tablets prescribed by your doctor or pharmacist to kill the type of blood fluke you have. Your doctor will prescribe a dose specifically for you. It is important to take all the tablets your doctor prescribed.
- Swallow the tablets with a full glass of water.
More instructions can be found in Section 4. How do I use BILTRICIDE? in the full CMI.
5. What should I know while using BILTRICIDE?
| Things you should do |
|
| Things you should not do |
|
| Driving or using machines |
|
| Looking after your medicine |
|
For more information, see Section 5. What should I know while using BILTRICIDE? in the full CMI.
6. Are there any side effects?
Common side effects: Vomiting, nausea, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, stomach pains, aching muscles, muscle tenderness or weakness, headache, dizziness, spinning sensation, hives (redness and itchiness of the skin) or rash, drowsiness, sleepiness, general feeling of being unwell, unusual tiredness or weakness, fever.
Serious side effects: rash; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body; shortness of breath, wheezing or trouble breathing; itching; seizures; palpitations and/or chest pain; bloody diarrhoea.
For more information, including what to do if you have any side effects, see Section 6. Are there any side effects? in the full CMI.
FULL CMI
BILTRICIDE® (BIL·tra·side)
Active ingredient(s): praziquantel
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
This leaflet provides important information about using BILTRICIDE. You should also speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you would like further information or if you have any concerns or questions about using BILTRICIDE.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
1. Why am I using BILTRICIDE?
2. What should I know before I use BILTRICIDE?
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
4. How do I use BILTRICIDE?
5. What should I know while using BILTRICIDE?
6. Are there any side effects?
7. Product details
1. Why am I using BILTRICIDE?
BILTRICIDE contains the active ingredient praziquantel. BILTRICIDE is an anthelmintic which treats parasitic infections.
BILTRICIDE is used for the treatment of schistosomiasis or bilharziasis, which is a chronic parasitic infestation in humans caused by blood flukes (worms). The flukes live in freshwater snails and you may have been infected if you swam or waded in water infested by larvae released from the snails. They are found in Africa (including Madagascar and Mauritius), the Middle East, India, Southeast Asia and South America.
The larvae penetrate the skin, most commonly on the feet, and mature into adult worms in the urinary bladder or the gut.
A rash may occur soon after infestation. Common symptoms of acute infestation are fever, night sweats, lethargy, headache, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, weight loss and a non-productive cough. You may pass blood in the urine.
Infestation with schistosoma parasites may cause no symptoms. However, they may also lead to chronic liver disease or chronic disorders of the urinary tract.
Eggs of the adult worms can occasionally be found in the brain or the spinal cord causing paralysis, or in the eyes, affecting your eyesight.
BILTRICIDE kills blood flukes by causing an immediate contraction and paralysis of the parasite; it also stops the parasite from being able to absorb and use sugars. The parasite then disintegrates with the help of the white blood cells and is passed from the body.
2. What should I know before I use BILTRICIDE?
Warnings
Do not use BILTRICIDE if:
- you are allergic to praziquantel, or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
- Always check the ingredients to make sure you can use this medicine.
- you are taking rifampicin (an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis or leprosy), dexamethasone (a corticosteroid) or anti-epileptic medicines.
- the infestation is found in your eyes, because killing the parasite may cause blindness.
Check with your doctor if you:
- have any other medical conditions
- any heart problems
- any kidney disease that causes you to pass little or no urine
- any problems with your liver, particularly, if your liver has been infected by blood flukes
- history of epilepsy
- skin nodules (slightly elevated lesions on or in the skin)
- take any medicines for any other condition
Use of BILTRICIDE may be associated with deterioration of your medical condition with symptoms similar to an allergic reaction. This is mainly seen in the acute phase of schistosomiasis (where the worms begin to produce eggs). This can lead to potentially life-threatening events such as lung failure, encephalopathy (disease of the brain), and/or cerebral vasculitis (narrowing or blockage of blood vessels in the brain).
If you take BILTRICIDE for an infestation in your brain or spinal cord, you may get severe headaches and fits. If the doctor wants to treat you for your infestation in the brain, you should be taken to hospital so that a specialist can monitor your treatment.
Your doctor may want to monitor you carefully or hospitalise you while you are taking BILTRICIDE. If you have not told your doctor or pharmacist about any of the above, tell them before you start taking BILTRICIDE.
During treatment, you may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It is important you understand these risks and how to monitor for them. See additional information under Section 6. Are there any side effects?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Check with your doctor if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant.
Your doctor can discuss with you the risks and benefits of using BILTRICIDE during pregnancy.
Talk to your doctor if you are breastfeeding or intend to breastfeed.
The active ingredient in BILTRICIDE passes into breast milk and there is a possibility that your baby may be affected. You should not breastfeed your baby on the day you take BILTRICIDE or for 3 days afterwards.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any medicines, vitamins or supplements that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Do not take BILTRICIDE if you are taking:
- rifampicin (an antibiotic used to treat tuberculosis and leprosy)
- efavirenz (a medicine used to treat HIV infections)
Some medicines may interfere with BILTRICIDE and affect how it works.
- dexamethasone (an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant)
- medicines for treating epilepsy
- cimetidine (a medicine used to treat high acid levels in your stomach, reflux and ulcers)
- chloroquine (an antimalarial medicine)
- ketoconazole or itraconazole (medicines used to treat fungal infections)
- erythromycin (an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections)
- ritonavir (a medicine used to treat HIV infections)
- grapefruit juice
These medicines may be affected by BILTRICIDE or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines.
Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines, vitamins or supplements you are taking and if these affect BILTRICIDE.
4. How do I use BILTRICIDE?
How much to take / use
- You must take all the BILTRICIDE tablets prescribed by your doctor or pharmacist to kill the type of blood fluke you have. Your doctor will prescribe a dose specifically for you. It is important to take all the tablets your doctor prescribed.
- The dose prescribed will usually be 20 mg for every kg of your body weight taken three times in the one day every four hours.
| Body weight in Kg | No. of tablets |
| 20-25 | ¾ |
| 26-33 | 1 |
| 34-41 | 1¼ |
| 42-48 | 1½ |
| 49-56 | 1¾ |
| 57-63 | 2 |
| 64-70 | 2¼ |
| 71-78 | 2½ |
| 79-86 | 2¾ |
- Swallow the tablets with a full glass of water.
- The tablet can be divided into 4 parts.
- Each part of the tablet has 150 mg of the active ingredient, allowing a precise dose to be given, depending on your weight.
- If you need to take ¼ of a tablet, it is easier if you break the tablet at one of the outer grooves. The simplest way to break the tablet is to put your thumbnail in the groove of the tablet.
- Follow the instructions provided when BILTRICIDE was prescribed, including the number of days it should be taken.
When to take / use BILTRICIDE
- BILTRICIDE should be used at about the same time each day.
- Taking it at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will also help you remember when to take it.
- Swallow the tablets preferably after eating a meal.
If you forget to use BILTRICIDE
BILTRICIDE should be used regularly at the same time each day. If you miss your dose at the usual time, take the dose as soon as you remember.
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to and seek your doctor's advice.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose you missed.
If you use too much BILTRICIDE
If you think that you have used too much BILTRICIDE, you may need urgent medical attention.
You should immediately:
- phone the Poisons Information Centre
(by calling 13 11 26), or - contact your doctor, or
- go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
You may need urgent medical attention.
If you take too many BILTRICIDE tablets, you should take a laxative, which works quickly.
5. What should I know while using BILTRICIDE?
Things you should do
If you are on corticosteroid therapy or if you are about to start taking any new medicine, especially medicines used to treat tuberculosis, leprosy, epilepsy, malaria, stomach acidity, reflux or ulcers, tell your doctor or pharmacist that you are taking BILTRICIDE.
See 3. What if I am taking other medicines? for examples of these medicines.
Remind any doctor, dentist or pharmacist you visit that you are using BILTRICIDE.
Things you should not do
- Do not stop using this medicine suddenly or lower the dosage without checking with your doctor.
If you stop taking it suddenly, your condition may worsen or you may have unwanted side effects. - Do not take BILTRICIDE to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
- Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Driving or using machines
Be careful before you drive or use any machines or tools until you know how BILTRICIDE affects you.
You should not drive or operate machinery on the day of treatment and for the next 24 hours because you may feel tired or dizzy after taking BILTRICIDE.
Drinking alcohol
Tell your doctor if you drink alcohol.
Looking after your medicine
- Keep your tablets in the bottle until it is time to take them. If you take the tablets out of the bottle they may not keep well.
- Keep your tablets in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Follow the instructions in the carton on how to take care of your medicine properly.
Store it in a cool dry place away from moisture, heat or sunlight; for example, do not store it:
- in the bathroom or near a sink, or
- in the car or on window sills.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date, take it to any pharmacy for safe disposal.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date.
Do not take this medicine if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
If the packaging is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
6. Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. If you do experience any side effects, most of them are minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any further questions about side effects.
Less serious side effects
| Less serious side effects | What to do |
Gastrointestinal:
Muscle-related:
Nervous system-related:
Skin-related:
General
| Speak to your doctor if you have any of these less serious side effects and they worry you. These are the more common side effects. It is often not clear, whether the side effects you experience are a result of taking BILTRICIDE, caused by the death of the parasites or are symptoms caused by the parasite. |
Serious side effects
| Serious side effects | What to do |
Allergic reaction eg.:
Skin-related:
Nervous system-related:
Gastrointestinal:
| Call your doctor straight away, or go straight to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. Serious side effects are uncommon. |
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that may be making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed here may occur in some people.
Side effects seem to happen more often and be more noticeable if you are infected with a large number of the parasites. Some patients may experience mild liver problems.
Reporting side effects
After you have received medical advice for any side effects you experience, you can report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration online at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you decide to stop taking any of your medicines.
7. Product details
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What BILTRICIDE contains
| Active ingredient (main ingredient) | Praziquantel 600 mg |
| Other ingredients (inactive ingredients) |
|
Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of these ingredients.
What BILTRICIDE looks like
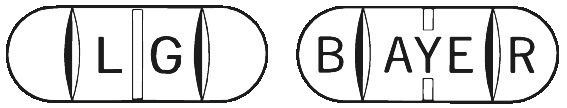
BILTRICIDE is available in bottles of 8 tablets. They are white to pale yellow oblong tablets, with three score lines, marked with 'BAYER' on one side and 'LG' on the reverse (Aust R 18845).
Who distributes BILTRICIDE
Bayer Australia Ltd
ABN 22 000 138 714
875 Pacific Highway
Pymble NSW 2073
Bayer New Zealand Limited
PO Box 2825
Shortland Street
Auckland 1140
New Zealand
See TGA website (www.ebs.tga.gov.au) for the latest Australian Consumer Medicine Information.
See MEDSAFE website (www.medsafe.govt.nz) for the latest New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information.
® Registered Trademark of the Bayer Group, Germany
© Bayer Australia Ltd.
All rights reserved.
This leaflet was prepared in July 2023.
Published by MIMS September 2023

 Biltricide should be swallowed whole with a little liquid, preferably after meals.
Biltricide should be swallowed whole with a little liquid, preferably after meals. It is often not clear whether the complaints reported by patients or the undesirable effects reported by the physician are caused by praziquantel itself (1. direct relation), or may be considered to be an endogenous reaction to the death of the parasites produced by praziquantel (2. indirect relation), or are symptomatic observations of the infestation (3. no relation). It may be difficult to differentiate between the possible variations 1, 2 and 3.
It is often not clear whether the complaints reported by patients or the undesirable effects reported by the physician are caused by praziquantel itself (1. direct relation), or may be considered to be an endogenous reaction to the death of the parasites produced by praziquantel (2. indirect relation), or are symptomatic observations of the infestation (3. no relation). It may be difficult to differentiate between the possible variations 1, 2 and 3.
