WHAT IS IN THIS LEAFLET
This leaflet answers some common questions about Magnevist. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor.
All diagnostic agents have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you using Magnevist against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about using this diagnostic agent, ask your doctor or radiologist.
Keep this leaflet.
You may need to read it again.
WHAT MAGNEVIST IS USED FOR
Magnevist is used at the same time as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to aid in the detection of abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, bones and muscles in adults; and in the brain and spinal cord in children and babies.
MRI is a form of medical diagnostic imaging that forms pictures after detecting water molecules in normal and abnormal tissues. This is done using a complex system of magnets and radiowaves.
Magnevist is a liquid that alters the way in which the MRI machine detects certain tissues within the body. Magnevist often makes the pictures clearer and often shows things that may not have been visible using MRI alone.
Magnevist is only available at MRI units for use in conjunction with MRI.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why Magnevist is being used in you.
Your doctor may be using it for another reason.
BEFORE YOU ARE GIVEN MAGNEVIST
When you must not be given it
You must not be given Magnevist if you have an allergy to:
- dimeglumine gadopentetate, the active ingredient in Magnevist
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin.
You must not be given Magnevist if you have severe disturbances of kidney function.
You must not be given Magnevist after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
The doctor will check this for you.
If you are not sure whether you should be given Magnevist, talk to your doctor/radiologist.
Before you are given it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Recent information shows that gadolinium (as in Magnevist) may accumulate in the brain after multiple use. To date, no adverse health outcomes associated with retention of gadolinium in the brain have been identified or reported.
Your doctor will:
- carefully consider the risks and benefits of repeated doses
- use the lowest dose
Tell your doctor if you have, or have had, any medical conditions especially the following:
- severe heart and circulatory disorders
- poor kidney function
- any allergies e.g. seafood allergies, hay fever, hives)
- bronchial asthma
- disease affecting red blood cells or anaemia (decrease in red blood cells)
- low blood pressure
- seizures
- liver disease.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, or think you may be pregnant, or if you are breastfeeding.
Your doctor can discuss with you the risks and benefits involved.
Tell your doctor if you have a heart pacemaker or any material implanted in your body
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell him/her before you are given Magnevist.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and Magnevist may interfere with each other. These include:
- beta-blockers (medicines used to treat high blood pressure or other heart conditions)
These medicines may be affected by Magnevist or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines. Your doctor will advise you.
Your doctor/radiologist has more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while receiving Magnevist.
HOW MAGNEVIST IS GIVEN
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor carefully.
They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions given, ask your doctor.
The radiologist (MRI specialist doctor) will advise the use of Magnevist if he/she feels that it is likely to assist the MRI examination in finding out more about your condition.
You should also fast for the last 2 hours prior to the examination but you may drink as usual. Further directions will be given by your doctor.
How much is given
The actual dosage of Magnevist that is right for you will be worked out by the radiologist and will depend on the region of your body to be examined. Normally only a single dose of about 15 to 20 mL of Magnevist will be required.
How it is given
Magnevist is injected by a doctor via a small needle into a vein, usually in the back of your hand or in front of your elbow.
When it is given
Magnevist will be administered immediately before your MRI examination.
How to prepare the MAGNEVIST syringe for injection
Glass syringe only:
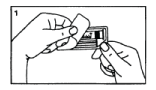
Peel the cover from the syringe tray and take the syringe and plunger rod out of the package.
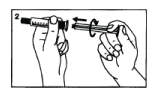
Screw the plunger into the syringe tightly
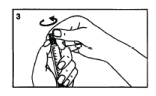
Break the first part of the protective grey cap.
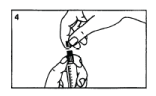
Remove the protective grey cap from the tip of the syringe.
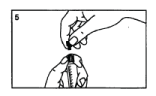
Remove the black stopper from the second part of the grey cap.
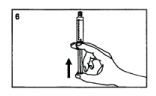
Remove the air in the syringe.
Plastic syringe only:
Hand injection:
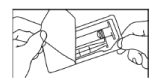
- Open the package
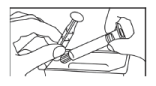
- Take the syringe and plunger rod out of the package
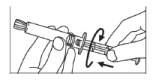
- Screw the plunger rod into the syringe
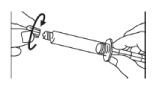
- Unscrew the cap from the syringe
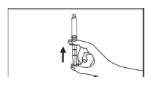
- Remove the air in the syringe
Injection with a power injector:
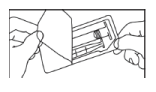
- Open the package
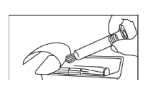
- Take the syringe out of the package
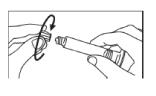
- Unscrew the cap from the syringe
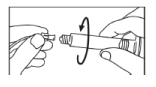
- Connect the tip of the syringe onto the tubing system and follow the device manufacturer’s instructions
If you are given too much (overdose)
As Magnevist is administered by a doctor, overdose is unlikely. If it does happen, the doctor will treat any symptoms that follow.
If you currently have a problem with your kidneys or liver, the doctor may decide to remove Magnevist from the body by means of a blood-cleansing procedure (dialysis).
Immediately tell your doctor or other medical staff or telephone the Poisons Information Centre (Australia: 13 11 26 or New Zealand: 0800 POISON or 0800 764 766) for advice if you think that you or anyone else may have been given too much Magnevist. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
You may need urgent medical attention.
AFTER HAVING MAGNEVIST
Things you must do
Follow carefully the directions given to you by your doctor and other medical staff.
Things to be careful of
Tell your doctor if you are going to have any laboratory tests.
Delayed reactions may occur. In this case Magnevist could prevent you from driving safely and the ability to operate any tools or machines may be impaired.
SIDE EFFECTS
Tell your doctor/radiologist as soon as possible if you do not feel well whilst receiving or after being given Magnevist.
All contrast media can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your doctor to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- dizziness
- headache
- unpleasant/altered taste
- nausea or vomiting
- local reaction around the injection site namely, pain, coldness, warmth, or a burning sensation.
The above list includes the more common side effects of Magnevist. They are usually mild and short-lived. If they persist or get worse, tell your doctor.
Tell your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following:
- conjunctivitis, watery eyes, disturbed vision, smell, hearing or speech
- ear or eye pain, ringing in the ears, pins and needles or a burning sensation
- agitation, confusion, or disorientation
- sensation of tickling, tingling, burning, pricking or numbness
- involuntary twitching
- uncontrolled shaking (convulsions)
- drowsiness , dizziness or light-headedness
- flushing, red or itchy skin; rash, or hives, swelling
- uncomfortable or irritated throat with swelling, or pain or a sensation of tightness
- coughing, sneezing, wheezing, hayfever
- breathlessness, difficulty breathing, or a change in breathing rate
- back pain or sore joints
- chest pain or an abnormal, fast or slow heart beat
- low or high blood pressure
- stomach pain or discomfort
- diarrhoea
- toothache, dry or sore mouth
- uncontrollable passing of urine, or feel an urgent need to pass urine
- chills, fever, generally feeling unwell, tired or thirsty
- discolouration and thickening of the skin (may feel “woody” and resemble an orange-peel texture), that may be painful and result in reduced joint mobility (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis).
These may be serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. Serious side effects are rare.
Some of these side effects could be the first signs of an allergic reaction. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
Allergic reactions occur more frequently in patients with an allergic disposition.
Severe reactions requiring emergency treatment can occur, causing low blood pressure, increase in heart rate, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face, lips or tongue leading to severe breathing difficulties and shock may occur.
Tell the doctor if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people. Rarely, delayed reactions can occur.
STORING MAGNEVIST
Storage
Keep Magnevist in the carton in order to protect from light until it is time to use it (applies to the glass presentations only).
Keep Magnevist in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C.
The MAGNEVIST syringes, vials and bottles should not be frozen.
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
What it looks like
Magnevist is a clear, colourless to slight yellow solution supplied in bottles and pre-filled glass and plastic syringes of various sizes.
Ingredients
Active ingredients:
- Magnevist – contains 469 mg dimeglumine gadopentetate per mL
Inactive ingredients:
- meglumine
- meglumine pentetate
- water for injections
- pentetic acid (2 mmol/L injection syringe only)
- sodium chloride (2 mmol/L injection syringe only)
Supplier
Made in Germany for:
Bayer Australia Limited
ABN 22 000 138 714
875 Pacific Highway
Pymble NSW 2073
Bayer New Zealand Limited
3 Argus Place, Hillcrest,
North Shore
Auckland 0627
Australian registration number
Glass vials, pre-filled syringes and bottle:
10 mL vial – AUST R 10697
30 mL vial– AUST R 59542
15 mL vial - AUST R 48494
20 mL vial - AUST R 48495
10 mL pre-filled syringe – AUST R 54671
15 mL pre-filled syringe – AUST R 54670
20 mL pre-filled syringe - AUST R – 54669
2 mmol/L pre-filled syringe – AUST R 98146
100 mL bottle – AUST R 90883
Plastic pre-filled syringes:
10 mL syringe – AUST R 54671
15 mL syringe – AUST R 54670
Not all presentations may be marketed in Australia and New Zealand.
Date of preparation
October 2017
See TGA website (www.ebs.tga.gov.au) for latest Australian Consumer Medicine Information.
See MEDSAFE website (www.medsafe.govt.nz) for latest New Zealand Consumer Medicine Information.
® Registered Trademark of Bayer AG, Germany
© Bayer Australia Ltd All rights reserved.



 If a strong clinical suspicion of a lesion persists despite a normal contrast enhanced MRI, a further injection of Magnevist 0.2 mL/kg or, in adults, even of 0.4 mL/kg bodyweight within 30 minutes, immediately following MRI, may increase the diagnostic yield of the examination.
If a strong clinical suspicion of a lesion persists despite a normal contrast enhanced MRI, a further injection of Magnevist 0.2 mL/kg or, in adults, even of 0.4 mL/kg bodyweight within 30 minutes, immediately following MRI, may increase the diagnostic yield of the examination.