What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about PANAFEN PLUS. It does not contain all the available information.
It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your pharmacist or doctor has weighed the risks of you taking PANAFEN PLUS against the benefits this medicine is expected to have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What PANAFEN PLUS is used for
This medicine is for the temporary relief of strong pain where ibuprofen alone is not effective.
You should only take this product for a maximum of 3 days at a time. If you need to take it for longer than 3 days, you should see your doctor for advice.
This medicine contains codeine which can cause addiction if you take it continuously for more than 3 days.
PANAFEN PLUS caplets contain the active ingredients ibuprofen and codeine phosphate. Ibuprofen belongs to a family of medicines called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS).
These medicines work by relieving pain, inflammation (swelling, redness, soreness) and fever. Codeine is an opioid analgesic that works in the brain and spinal cord to relieve pain.
PANAFEN PLUS relieves strong pain and discomfort associated with migraine or tension headache, period pain, toothache, cold & flu symptoms, back or muscular pain, arthritis and neuralgia. It also reduces any fever associated with these pain conditions.
PANAFEN PLUS should not be used in children under the age of 18 years.
Your doctor or pharmacist may have given you this medicine for another use.
If you need more information ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Do not use PANAFEN PLUS if
When you must not take it
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS if you are under the age of 18 years.
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS if you have an allergy to:
- ibuprofen, codeine or other opioid pain reliever
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
- aspirin
- any other NSAID medicine.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to these medicines may include:
- asthma, wheezing or shortness of breath
- swelling of the face, lips or tongue which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing
- fainting
- hives, itching or skin rash.
If you are allergic to aspirin or NSAID medicines and take PANAFEN PLUS, these symptoms may be severe.
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS if you are also taking any other medicines that contain NSAIDS, whether prescribed by your doctor or obtained without prescription.
Many medicines used to treat headache, migraine, dental or period pain and other aches and pains contain aspirin or NSAID medicines. If you are not sure if you are taking any of these medicines, ask your pharmacist.
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS during pregnancy.
PANAFEN PLUS should not be taken whilst breast-feeding.
The use of codeine containing products while breast-feeding may harm your baby.
Do not take PANAFEN Plus if you have been told by your doctor that you breakdown codeine rapidly since the following side effects may develop: feeling sick, vomiting, constipation, decreased or lack of appetite, feeling tired or sleeping for longer than usual, feeling confused and have breathing problems.
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS if:
- you are vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds
- you are bleeding from the back passage (rectum), have black sticky bowel motions (stools) or bloody diarrhoea
- you have a stomach or duodenal ulcer, perforation or bleeding of the stomach or have had one in the past
- you have asthma that is sensitive to aspirin or NSAIDs
- you have chronic constipation
- you have shallow breathing
- you have severe diarrhoea
- you consume regular and heavy amounts of alcohol
- you have heart failure
- you have liver or kidney disease
- you are using NSAIDs including COX-2 specific inhibitors, e.g. Celecoxib (Celebrex), Meloxicam (Mobic)
- patients undergoing treatment of perioperative pain in setting of coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG).
PANAFEN PLUS should not be used if you have kidney problems or severe liver problems.
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS after the expiry date (EXP) printed on the pack.
If you take this medicine after the expiry date has passed, it may have no effect at all, or worse, have an entirely unexpected effect.
Do not take PANAFEN PLUS if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Do not use this medicine to treat any other complaint unless your doctor or pharmacist says it is safe. Do not give this medicine to anyone else even if they have the same symptoms as you.
Before you start to take it
You must tell your pharmacist or doctor if:
- you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant
PANAFEN PLUS is not recommended for use during pregnancy. PANAFEN PLUS is not recommended in women attempting to conceive, as NSAIDS like ibuprofen may impair fertility in women. This effect is reversible upon stopping the medicine. - you are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed
PANAFEN PLUS is not recommended if you are breast-feeding. - you have any medical conditions, especially the following:
- a history of stomach or duodenal ulcer
- stomach problems or recent stomach surgery
- liver or kidney disease
- heart failure including
- swelling of feet or ankles
- high blood pressure
- asthma or have suffered in the past from asthma or allergic disease
- bowel or intestinal problems including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
- history of cholecystectomy
- had an operation to remove your gallbladder
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- a history of drug dependence
- thyroid problems or low blood pressure
- head injury or raised intracranial pressure
- prostate problems. - you currently have an infection
If you take Panafen Plus while you have an infection the medicine may hide some of the signs of an infection. This may make you think, mistakenly, that you are better or that it is not serious. - you have liver disease
Remain alert for signs and/or symptoms of liver toxicity (e.g. nausea, fatigue, lethargy, itching, yellowing of the skin and/or eyes (jaundice), abdominal tenderness in the right upper quadrant and "flu-like" symptoms).
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor about taking this medicine if you are over 65 years of age.
Taking this medicine may increase the risk of you getting stomach, heart or kidney problems.
Ibuprofen may be associated with an increased risk of serious cardiovascular events, including heart attack and stroke, which are more likely with high doses and prolonged treatment. There may be a greater risk for patients with cardiovascular disease, history of atherosclerotic disease or cardiovascular risk factors. Even in the absence of previous cardiovascular symptoms, remain alert for such cardiovascular events. Talk to your doctor about signs and/or symptoms of serious cardiovascular toxicity and the steps to take if they occur.
Taking other medicines
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may interfere with each other. These include:
- aspirin, salicylates or other NSAID medicines including COX-2 specific inhibitors
- warfarin or other medicines used to stop blood clots or thin the blood including low dose aspirin
- digoxin, a medicine to treat heart failure
- medicines that are used to treat high blood pressure
- diuretics, also called fluid or water tablets
- methotrexate, a medicine to treat arthritis and some cancers
- cyclosporine, a medicine that suppresses the immune system
- corticosteroids which reduce the activity of your immune system
- quinolone antibiotics
- zidovudine, a medicine used to treat HIV infection
- lithium and other medicines used to treat depression, e.g. MAOIs (even if taken within the last 14 days) and SSRIs
- anticholinergic medicines such as those used to relieve stomach cramps, to prevent travel sickness and to treat Parkinson's disease
- medicines used to treat diarrhoea (e.g. kaolin, pectin, loperamide)
- metoclopramide, a medicine used to treat nausea and vomiting
- antidiabetic medications
- other opioid pain killers
- medicines to help you relax, sleep or relieve anxiety, such as barbiturates and sedatives
- phenothiazines and antipsychotic agents used to treat mental disorders
- probenecid, a medicine to treat gout
- phenytoin, a medicine to treat epilepsy
- quinidine, a medicine to treat certain heart conditions.
These medicines may be affected by PANAFEN PLUS or may affect how well it works. You may need to take different amounts of your medicine, or you may need to take different medicines. Your doctor or pharmacist will advise you.
Your pharmacist and doctor have more information on medicines to avoid or be careful with while taking PANAFEN PLUS.
How to take PANAFEN PLUS
How much to take
Take 2 caplets of PANAFEN PLUS then, if necessary, 1 or 2 caplets every 4 hours.
Do not take more than six caplets in 24 hours.
If symptoms persist or worsen, please consult your doctor.
This product should be taken at the lowest dose for the shortest time necessary to relieve your symptoms. Taking this medicine regularly for a long time can lead to addiction.
Do not take for more than 3 days without asking your doctor.
If you do not understand the instructions on the pack, ask your pharmacist or doctor for help.
PANAFEN PLUS is not recommended for children under 18 years.
Do not exceed the stated dose and do not take more frequently than every 4 hours.
Do not take this product with any other product containing ibuprofen or codeine.
How to take it
Take PANAFEN PLUS by mouth with fluid. It may also be taken with or immediately after food.
How long to take it
You should not take PANAFEN PLUS for more than 3 days.
PANAFEN PLUS should not be used for more than a few days at a time unless on medical advice.
If your symptoms persist, get worse or new symptoms develop, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre telephone 13 11 26 (Australia) or 0800 764 766 (New Zealand) for advice or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much PANAFEN PLUS.
Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention because of the risk of liver failure and breathing problems. Keep telephone numbers of these places handy.
If you take too much of this medicine you may experience the following:
- nausea or an upset stomach
- vomiting and gastric irritation
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- very slow, laboured breathing.
- blurred vision
- ringing in the ears
- rapid, uncontrollable movements of the eyes.
In rare cases you may experience the following:
- excitability
- convulsions
- unconsciousness.
While you are taking PANAFEN PLUS
Things you must do
Take PANAFEN PLUS exactly as your pharmacist or doctor has told you to.
Tell all your doctors, dentists and pharmacists that you are taking PANAFEN PLUS.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you become pregnant while taking PANAFEN PLUS.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking PANAFEN PLUS.
If you are going to have surgery, tell your doctor you are taking PANAFEN PLUS.
Things you must not do
Do not give PANAFEN PLUS to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not use PANAFEN PLUS to treat any other complaints.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how PANAFEN PLUS affects you.
PANAFEN PLUS may cause dizziness, light-headedness, drowsiness, fatigue or visual disturbances in some people. If this occurs, do not drive or operate machinery.
If you drink alcohol, the dizziness, light-headedness or drowsiness may be worse.
Products containing codeine should not be taken for prolonged periods.
Codeine may be habit-forming.
About 5-10% of people are poor metabolisers of codeine and PANAFEN PLUS may not work as well if you are one of those people.
Products containing ibuprofen should not be used for prolonged periods.
Excessive use can be harmful and increase the risk of heart attack, stroke or liver damage.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while taking PANAFEN PLUS.
Like other medicines, PANAFEN PLUS can cause some side effects. If they occur, they are most likely to be minor and temporary. However, sometimes they are serious and need medical attention.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- stomach upset including nausea (feeling sick)
- vomiting
- heartburn
- indigestion
- diarrhoea, pain in the stomach
- dizziness, light-headedness, drowsiness
- constipation
- cough suppression
- headache
- hearing disturbance.
These are the more common side effects of PANAFEN PLUS and are usually mild and short-lived.
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if you notice any of the following:
- shallow breathing or shortness of breath.
The above list includes serious side effects that may require medical attention. Serious side effects are rare.
If any of the following happen, stop taking PANAFEN PLUS and tell your doctor immediately or go to Casualty at your nearest hospital:
- vomiting blood or material that looks like coffee grounds
- bleeding from the back passage, black sticky bowel motions (stools) or bloody diarrhoea
- swelling of the face, lips or tongue which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing
- you experience breathlessness and/or swelling of legs or feet
- you experience a skin rash or peeling, or mouth ulcers
- asthma, wheezing, shortness of breath, pain or tightness in the chest
- you have previously had gallbladder removal surgery and experience severe abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
- sudden or severe itching, skin rash, hives, skin peeling
- you experience unexplained bruising or bleeding, fever, sore throat, extreme pallor or weakness
- your existing bowel disease (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease) worsens
- you have an existing autoimmune disorder (e.g. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease) and develop a stiff neck, headache, nausea, vomiting, fever or feel disorientated
- you pass less or more urine than normal, your urine is cloudy, there is blood in your urine, or you experience pain in the back and/or swelling (particularly of the legs)
- you experience liver problems including jaundice, symptoms could include yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
These are very serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation. These side effects are rare.
Some people may get other side effects while taking PANAFEN PLUS. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that worries you.
Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
After taking PANAFEN PLUS
Storage
Keep the caplets in the pack until it is time to take them.
If you take them out they will not keep well.
Keep the caplets in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines. Do not leave PANAFEN PLUS in the car on hot days.
Keep PANAFEN PLUS where children cannot reach them. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Do not store PANAFEN PLUS or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink.
Disposal
When you stop taking PANAFEN PLUS or it has passed its expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any caplets that are left over.
This is not all the information that is available on PANAFEN PLUS. If you have any more questions or are not sure about anything, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Product description
What it looks like
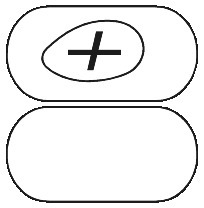
PANAFEN PLUS caplets are white capsule shaped tablets marked on one side with a "+" sign surrounded by an oval.
They come in cartons of 15 and 30 caplets.
Ingredients
Active ingredients:
Each PANAFEN PLUS caplet contains:
- Ibuprofen 200 mg
- Codeine phosphate 12.8 mg.
Other ingredients:
- Cellulose-microcrystalline
- Vegetable oil-hydrogenated
- Sodium starch glycollate
- Silica-colloidal anhydrous
- Lactose
- Cellulose-powdered
- Hypromellose
- Macrogol 400.
Manufacturer/Supplier
PANAFEN PLUS caplets are supplied in Australia and New Zealand by:
GlaxoSmithKline Consumer Healthcare Australia Pty Ltd
82 Hughes Avenue, Ermington NSW and Auckland, New Zealand
AUST R 106616
Date of preparation: January 2016.
PANAFEN is a registered trade mark of the GSK group of companies or its licensor.