What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some of the common questions people ask about ARIMIDEX. It does not contain all the information that is known about ARIMIDEX.
It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor will have weighed the risks of you taking ARIMIDEX against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What ARIMIDEX is used for
ARIMIDEX is used to treat breast cancer in women who no longer have their menstrual periods either naturally, due to their age or after surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
ARIMIDEX is a non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor, which reduces the amount of oestrogen (female sex hormone) made by the body. In some types of breast cancer, oestrogen can help the cancer cells grow. By blocking oestrogen, ARIMIDEX may slow or stop the growth of cancer.
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why ARIMIDEX has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed ARIMIDEX for another reason.
ARIMIDEX is only available with a doctor's prescription.
ARIMIDEX is not addictive
Before you take ARIMIDEX
When you must not take it
Do not take ARIMIDEX if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant. ARIMIDEX may affect your developing baby if you take it during pregnancy.
Do not breastfeed while taking ARIMIDEX. Your baby can take in ARIMIDEX from breast milk if you are breastfeeding.
Do not take ARIMIDEX if you have an allergy to:
- Anastrozole, the active ingredient of ARIMIDEX
- Any of the other ingredients of ARIMIDEX listed at the end of this leaflet
- Other anti-oestrogen medicines.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty in breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or any other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not take ARIMIDEX if you are still having menstrual periods.
ARIMIDEX should only be taken by women who are no longer having menstrual periods.
Do not take ARIMIDEX if you are a man. Men are not normally treated with ARIMIDEX.
Do not give ARIMIDEX to a child. ARIMIDEX is not recommended for use in children.
Do not take ARIMIDEX after the use by (expiry) date printed on the pack. Do not take ARIMIDEX if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal
Do not use it to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not give this medicine to anyone else.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if you have any allergies to the following:
- Any medicines
- Any other substances, such as foods, preservatives or dyes
Tell your doctor if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions:
- Liver problems
- Kidney problems
- Osteoporosis, a family history of osteoporosis or risk factors for developing osteoporosis (such as smoking, a diet low in calcium, poor mobility, a slight build or treatment with steroid medicines)
Aromatase inhibitors may decrease bone mineral density (BMD) in women who have been through menopause, with a possible increased risk of fractures. Your doctor should discuss with you your treatment options for managing this possible increased risk of fractures.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell him/her before you start taking ARIMIDEX.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines should not be taken with ARIMIDEX. These include:
- Tamoxifen, a medicine used to treat breast cancer
- Any medicine that contains oestrogen such as medicines used in Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) or oral contraceptives
- Any health food products that contain natural oestrogens used for post-menopausal symptoms.
- Medicines from a class called "Luteinising Hormone Releasing Hormone (LHRH) agonists", such as goserelin or leuprorelin.
Talk to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any concerns or questions about taking ARIMIDEX.
Your doctor or pharmacist have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
How to take ARIMIDEX
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
Your doctor or pharmacist will tell you how many tablets you will need to take each day. This depends on your condition and whether or not you are taking any other medicines.
If you do not understand the instructions on the box, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How much to take
The usual dose is one tablet every day.
When to take it
Take ARIMIDEX at about the same time each day. Taking it at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will also help you remember when to take it.
Swallow ARIMIDEX tablets whole, with a glass of water.
It does not matter if you take ARIMIDEX before, with or after food.
How long to take it
Continue taking ARIMIDEX for as long as your doctor or pharmacist tells you.
ARIMIDEX helps to control your condition, but does not cure it. Therefore you must take ARIMIDEX every day. Do not stop taking it unless your doctor tells you to - even if you feel better.
If you forget to take it
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, as long as it is 12 hours before the next dose is due. If it is less than 12 hours to the next dose, do not take the dose you have missed.
Do not double the dose to make up for the dose that you missed.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering when to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much ARIMIDEX. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are taking it
Things you must do
Be sure to keep all your appointments with your doctor so your progress can be checked.
Tell any other doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking ARIMIDEX.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, tell your doctor, dentist or pharmacist that you are taking ARIMIDEX.
If you go into hospital, please let the medical staff know that you are taking ARIMIDEX.
Things you must not do
Do not give ARIMIDEX to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not take ARIMIDEX to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not stop taking ARIMIDEX unless you have discussed it with your doctor.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how ARIMIDEX affects you. Some patients may occasionally feel weak or sleepy.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking ARIMIDEX.
ARIMIDEX helps most postmenopausal women with breast cancer, but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people.
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. Side effects may happen at the start of treatment or they may happen after you have been taking your medicine for some time. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
If you get any side effects do not stop taking ARIMIDEX without first talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
If any of the following happen tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- Sudden signs of allergy such as shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty in breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or any other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
- Severe skin reactions with lesions, ulcers or blisters.
- Liver pain or swelling and/or a general feeling of unwell with or without jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
These are serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
Serious side effects are uncommon or rare.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- Hot flushes
- Feeling weak or a lack of energy
- Feeling sleepy
- Joint pain or stiffness
- Bone loss (osteoporosis)
- Vaginal dryness
- Vaginal bleeding
- Thinning of hair (hair loss)
- Mild skin rash
- Feeling sick (nausea)
- Diarrhoea
- Headache
- Loss of appetite (anorexia)
- Vomiting
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (tingling, pain, coldness, weakness in parts of hand)
- Pins and needles
- Loss of taste or changing taste of food or drink
- Feeling depressed
ARIMIDEX may be associated with changes in your blood, urine or liver. Your doctor may want to perform tests from time to time to check on your progress and detect any unwanted side effects.
These are the more common side effects of ARIMIDEX. Mostly these are mild to moderate in nature.
Uncommon side effects can include , trigger finger which is a condition in which one of your fingers or your thumb catches in a bent position.
Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Other side effects not listed may occur in some people.
Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
After taking it
Storage
Keep your tablets in the blister pack until it is time to take them. If you take ARIMIDEX out of the blister pack it will not keep well.
Keep it in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30 degrees C.
Do not store it or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Do not leave it on a window-sill or in the car on hot days. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Disposal
Ask your pharmacist what to do with any tablets you have left over if your doctor tells you to stop taking them, or you find that the expiry date has passed.
Product description
What ARIMIDEX looks like
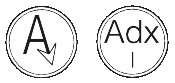
ARIMIDEX 1 mg is a round, white, biconvex film-coated tablet with the following markings:
They are marked with a letter 'A' with an arrow head attached to the right leg of the 'A' on one side and marked Adx1 on the other
Ingredients
Each ARIMIDEX tablet contains 1 mg of anastrozole as the active ingredient, and the following inactive ingredients:
- Lactose monohydrate
- Povidone
- Sodium starch glycolate
- Magnesium stearate (E572)
- Hypromellose
- Macrogol 300
- Titanium dioxide (E171)
ARIMIDEX comes in a blister pack containing 30 tablets.
Distributor
AstraZeneca Pty Ltd
ABN 54 009 682 311
66 Talavera Road
MACQUARIE PARK NSW 2113
Telephone: 1800 805342
This leaflet was prepared on 05 November 2021
Australian Registration Number:
AUST R 54672
Doc ID-002111414 v6
ARIMIDEX® is a trademark of the AstraZeneca group of companies.
Published by MIMS January 2022

 In a large phase III study conducted in 9366 postmenopausal women with operable breast cancer treated for 5 years, ischaemic cardiovascular events (consisting mainly of angina pectoris) in the on treatment period were reported more frequently in patients treated with Arimidex compared to those treated with tamoxifen (mainly associated with patients with pre-existing ischaemic heart disease), although the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.1224).
In a large phase III study conducted in 9366 postmenopausal women with operable breast cancer treated for 5 years, ischaemic cardiovascular events (consisting mainly of angina pectoris) in the on treatment period were reported more frequently in patients treated with Arimidex compared to those treated with tamoxifen (mainly associated with patients with pre-existing ischaemic heart disease), although the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.1224). Compared with tamoxifen, anastrozole treatment was associated with a significantly increased incidence of fractures (34 cases vs. 16 cases; odds ratio (OR) = 2.14 (95% CI: 1.14-4.17; p = 0.015)), but with a reduced incidence of thromboses (3 vs. 12 cases; OR = 0.25 (95% CI: 0.04-0.92; p = 0.034)).
Compared with tamoxifen, anastrozole treatment was associated with a significantly increased incidence of fractures (34 cases vs. 16 cases; odds ratio (OR) = 2.14 (95% CI: 1.14-4.17; p = 0.015)), but with a reduced incidence of thromboses (3 vs. 12 cases; OR = 0.25 (95% CI: 0.04-0.92; p = 0.034)). Arimidex was associated with an increased incidence of lipid disorders and gastrointestinal events, but with a reduced incidence of gynaecological events, when compared with tamoxifen.
Arimidex was associated with an increased incidence of lipid disorders and gastrointestinal events, but with a reduced incidence of gynaecological events, when compared with tamoxifen.



 Overall survival was a secondary endpoint in the ATAC study. The 100 month analysis of this study demonstrated that overall survival in the Arimidex arm and the tamoxifen arm were not significantly different. Similar overall survival was observed for both the ITT group and hormone receptor positive subgroup (see Table 4). At the 100 month follow up the mean age of the surviving population was 72 years, with nonbreast cancer deaths accounting for 42 and 46% of total mortality in the ITT and hormone receptor positive subgroup respectively.
Overall survival was a secondary endpoint in the ATAC study. The 100 month analysis of this study demonstrated that overall survival in the Arimidex arm and the tamoxifen arm were not significantly different. Similar overall survival was observed for both the ITT group and hormone receptor positive subgroup (see Table 4). At the 100 month follow up the mean age of the surviving population was 72 years, with nonbreast cancer deaths accounting for 42 and 46% of total mortality in the ITT and hormone receptor positive subgroup respectively. Serious adverse events continued to be collected during the off treatment follow-up. Overall the number of treatment related serious adverse events remained lower with anastrozole than with tamoxifen for the active follow-up period, and was significantly lower during treatment and similar after treatment completion. The incidence of cardiovascular events reported was similar in the Arimidex and tamoxifen arms (3.9% vs. 3.7%, respectively) in the 100 month analysis.
Serious adverse events continued to be collected during the off treatment follow-up. Overall the number of treatment related serious adverse events remained lower with anastrozole than with tamoxifen for the active follow-up period, and was significantly lower during treatment and similar after treatment completion. The incidence of cardiovascular events reported was similar in the Arimidex and tamoxifen arms (3.9% vs. 3.7%, respectively) in the 100 month analysis. Demographics and other baseline characteristics were similar for the two treatment groups for both trials. The hormone receptor status at entry for all randomised patients in trials 0027 and 0030 is summarised in Table 6.
Demographics and other baseline characteristics were similar for the two treatment groups for both trials. The hormone receptor status at entry for all randomised patients in trials 0027 and 0030 is summarised in Table 6.
 Chemical name: 2,2'-[5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-phenylene]bis(2-methylpropiononitrile).
Chemical name: 2,2'-[5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-phenylene]bis(2-methylpropiononitrile).