What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Avil. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor or pharmacist has weighed the risks of you taking this medicine against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
What Avil is used for
Avil Tablets contain pheniramine maleate, a medicine used to treat allergic conditions such as hayfever, runny nose, itching skin and skin rashes. It is also used in the prevention and treatment of nausea, vomiting and dizziness due to inner ear disorders (eg Meniere's disease) and travel sickness.
Avil is one of a group of medicines called 'antihistamines' which works by blocking the action of histamine.
Before you take Avil
When you must not take it
Do not take Avil if you:
- are taking an antidepressant medicine known as a MAO Inhibitor
- are male and you have an enlarged prostate
Do not give Avil to a premature or newborn baby.
Do not take Avil if you are allergic to it or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet. Some symptoms of an allergic reaction include skin rash, itching, asthma, wheezing, shortness of breath or swelling of the fact, lips or tongue, which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing, fainting.
Contains lactose and sugars.
Do not take it after the expiry date (EXP) printed on the pack. If you take it after the expiry date has passed, it may not work as well.
Do not take it if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
- any other medicines
- any other substances, such as foods, preservatives or dyes.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant. Your doctor or pharmacist will discuss the risk and benefits of taking it if you are pregnant.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. If there is a need to consider Avil while you are breastfeeding, your doctor or pharmacist will discuss with you the benefits and risks of taking it.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have or have had any medical conditions, especially the following:
- an enlarged prostate
- glaucoma (high pressure in the eye)
- breathing problems, including asthma or bronchitis
- heart disease
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you plan to have surgery.
If you have not told your doctor or pharmacist about any of the above, tell them before you take Avil.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food store.
Some medicines and Avil may interfere with each other. These include:
- antidepressants known as MAO inhibitors
- atropine and other anticholinergic drugs (such as medicines used to relieve stomach cramps or spasms, to prevent travel sickness and to treat Parkinson's disease)
- alcohol
- sedative drugs
Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or to avoid while taking Avil.
Avil may cause drowsiness and may increase the effects of alcohol and other sedative drugs. If affected, do not drive a motor vehicle or operate machinery. You might get used to the sedative effect after a few days of treatment, however you may prefer to change to a non-sedating antihistamine.
Please discuss this option with your pharmacist.
How to take Avil
How much to take
Adults and children over 10 years:
Half to 1 tablet up to 3 times daily.
Children 5-10 years:
Half a tablet up to 3 times daily.
Not recommended for children under 5 years of age.
To prevent travel sickness, it is recommended that the first dose be taken at least 30 minutes before travelling.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure of the correct dose for you. They will tell you exactly how much to take.
How to take it
Avil should be swallowed with plenty of water. Do not chew them.
When to take it
Avil should be taken with or soon after food. Do not take the medicine on an empty stomach.
If you are taking Avil to prevent travel sickness, take a dose at least 30 minutes before travelling.
If you are not sure when to take Avil, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
How long to take it
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure how long to take this medicine for.
If you forget to take or give a dose
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to. Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember, and then go back to taking your dose as you would normally. Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much Avil.
Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are taking Avil
Things you must do
Tell all the doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking Avil.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking Avil.
If you need to have an allergy test, tell your doctor that you are taking Avil.
If you become pregnant while taking Avil, tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Things you must not do
Do you take more than the recommended dose unless your doctor or pharmacist tells you to.
Things to be careful of
Avil can cause drowsiness so you should not drive a motor vehicle or operate machinery after taking a dose. This effect may decrease with time.
Side effects
All medicines can have some unwanted side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. Your doctor or pharmacist has weighed the risks of using this medicine against the benefits they expect it will have for you. Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking Avil.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- drowsiness
- nervousness, irritability, incoordination, lack of concentration
- tiredness or weariness
- dizziness
- buzzing, hissing, whistling, ringing or other persistent noise in the ears
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhoea
- stomach pain
- difficulty passing urine
- trouble sleeping
- shaking
- loss of appetite
- dryness of mouth
- constipation
- looking pale
Tell your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following:
- changes in your usual behaviour or mood
- severe sedation, confusion or restlessness
- waves of sudden severe stomach pain
- hallucinations
- vision problems
- irregular heart beat
- headache
- frequent infections such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers
If any of the following happen, stop taking this medicine and tell your doctor immediately, or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- swelling of the face, lips, mouth or throat, which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing
- hives
- fainting
- yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Agitation and convulsions, and sometimes death, especially in children and restlessness, disorientation and hallucinations in adults, are common symptoms following overdose.
These may be serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. Serious side effects are rare.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
After taking Avil
If you have any queries about any aspect of your medicine, or any questions regarding the information in this leaflet, discuss them with your doctor or pharmacist.
Storage
Keep your tablets in the blister pack until it is time to take them. If you take the tablets out of the box or the blister pack, they may not keep well.
Keep Avil in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C. Do not store Avil or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car or on window sills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking it or the expiry date has passed, ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over.
Return any unused medicine to your pharmacist.
Product description
What it looks like
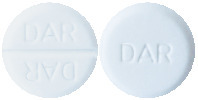
Avil tablets are round white tablets with DAR on one side of the tablet and DAR on each side of a score line on the other side of the tablet. They come in packs of 10 and 50* tablets.
*Packs currently not marketed in Australia
Ingredients
Active ingredients:
Avil tablets contain the active ingredient pheniramine maleate.
There is 45.3 mg of pheniramine maleate in every tablet.
Inactive ingredients:
- maize starch
- lactose monohydrate
- magnesium stearate
- pregelatinized maize starch
- silicon dioxide
Avil preparations do not contain gluten, tartrazine or azo dyes.
Sponsor
Avil tablets supplied in Australia by:
sanofi-aventis australia pty ltd
12-24 Talavera Road
Macquarie Park NSW 2113
Australian Register Number 191053
This leaflet was prepared in February 2020
® Registered Trademark
avil-ccdsv01-cmiv2-13feb20
Published by MIMS July 2020