SUMMARY CMI
DIZOLE®
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) summary
The full CMI on the next page has more details. If you are worried about using this medicine, speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
1. Why am I using DIZOLE?
DIZOLE contains the active ingredient fluconazole. DIZOLE is used to treat certain fungal and yeast infections that cause thrush in the mouth, food pipe or vagina (also called candida or monilia); tinea of the body, groin or feet and meningitis, where the membrane around the brain and spinal cord are inflamed due to infection.
For more information, see Section 1. Why am I using DIZOLE? in the full CMI.
2. What should I know before I use DIZOLE?
Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to DIZOLE or any of the ingredients listed at the end of the CMI.
Talk to your doctor if you have any other medical conditions, take any other medicines, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding. For more information, see Section 2. What should I know before I use DIZOLE? in the full CMI.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Some medicines may interfere with DIZOLE and affect how it works.
A list of these medicines is in Section 3. What if I am taking other medicines? in the full CMI.
4. How do I use DIZOLE?
- For Adults: The dose will depend on your infection and how you respond to DIZOLE. It usually ranges from 50 to 400 mg once daily.
- For Children: The dose for a child will depend on body weight and usually ranges from 3 mg to 12 mg per kilogram of body weight. In very young children (below 4 weeks of age), DIZOLE is usually given every second or third day.
- Swallow the capsules whole with a glass of water.
More instructions can be found in Section 4. How do I use DIZOLE? in the full CMI.
5. What should I know while using DIZOLE?
| Things you should do |
|
| Things you should not do |
|
| Driving or using machines |
|
| Drinking alcohol |
|
| Looking after your medicine |
|
For more information, see Section 5. What should I know while using DIZOLE? in the full CMI.
6. Are there any side effects?
The most common side effects of your medicine include nausea or feeling sick, stomach pain, headache and acne. They are usually mild and short-lived. Serious side effects include rash, swelling of the face, irregular heart beat and increased sweating.
For more information, including what to do if you have any side effects, see Section 6. Are there any side effects? in the full CMI.
FULL CMI
DIZOLE®
Active ingredient(s): fluconazole
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
This leaflet provides important information about using DIZOLE. You should also speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you would like further information or if you have any concerns or questions about using DIZOLE.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
1. Why am I using DIZOLE?
2. What should I know before I use DIZOLE?
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
4. How do I use DIZOLE?
5. What should I know while using DIZOLE?
6. Are there any side effects?
7. Product details
1. Why am I using DIZOLE?
DIZOLE contains the active ingredient fluconazole. Fluconazole belongs to a group of medicines called azole antibiotics.
It works by preventing the growth of the fungal and yeasts organisms causing your infection.
DIZOLE is used to treat certain fungal and yeast infections that cause:
- thrush in the mouth, food pipe or vagina (also called candida or monilia)
- tinea of the body, groin or feet
- meningitis, where the membrane around the brain and spinal cord are inflamed due to infection.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you.
Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
DIZOLE is available only with a doctor's prescription.
This medicine is not addictive.
2. What should I know before I use DIZOLE?
Warnings
Do not use DIZOLE if:
- you are allergic to fluconazole, or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet. Always check the ingredients to make sure you can use this medicine.
- you have an allergy to any other azole antifungals related to fluconazole such as itraconazole (Sporanox), ketoconazole (Nizoral), miconazole (Daktarin), clotrimazole (Canesten).
- Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing; swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body; rash, itching or hives on the skin.
- the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering or after the expiry date printed on the pack. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
You must not be given DIZOLE if you are taking any of the following medicines
- terfenadine or astemizole (a medicine used to treat allergy)
- cisapride (Prepulsid), a medicine used to treat stomach problems.
- erythromycin (a medicine used to treat infections)
- pimozide (a medicine used to treat mental illness)
- quinidine (a medicine used to treat irregular heartbeat)
Check with your doctor if you:
- have allergies to any other medicines, foods, dyes or preservatives.
- have any other medical conditions
- take any medicines for any other condition
- have liver problems
- have heart problems
- have kidney problems
Your doctor may need to monitor the function of the liver using blood tests. Be sure to follow the doctor's advice if regular checks on your/ your child's liver are recommended.
During treatment, you may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It is important you understand these risks and how to monitor for them. See additional information under Section 6. Are there any side effects?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Check with your doctor if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant.
DIZOLE use should be avoided during pregnancy except on doctor's advice for severe or life-threatening infections. Effective contraception should be used in women of childbearing potential and should continue throughout the treatment period and for approximately 1 week after the final dose. Your doctor can discuss with you the risks and benefits involved.
Talk to your doctor if you are breastfeeding or intend to breastfeed.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start taking DIZOLE.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any medicines, vitamins or supplements that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines should not be taken with DIZOLE.
These are listed under Section 2. What should I know before I use DIZOLE.
Some medicines may interfere with DIZOLE and affect how it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines. These include:
- certain medicines for diabetes such as tolbutamide, glibenclamide (eg. Daonil, Glimel) and glipizide (eg. Minidiab, Melizide)
- rifampicin (eg Rifadin, Rimycin) or rifabutin (eg. Mycobutin), antibiotics used to treat infections
- zidovudine (eg Retrovir), a medicine used to treat patients with HIV infection
- amphotericin B (amphotericin) (eg. Fungilin), a medicine used to treat fungal infection
- azithromycin
- saquinavir
- voriconazole
- some drugs used for heart problems, such as amiodarone or verapamil
- ciclosporin (eg Neoral, Sandimmun), sirolimus (eg. Rapamune) or tacrolimus (eg. Prograf), or tofacitinib medicines used to prevent organ transplant rejection or to treat certain problems with the immune system
- some medicines used to lower cholesterol, such as atorvastatin, simvastatin or fluvastatin
- cyclophosphamide monohydrate, vincristine, vinblastine, olaparib or ibrutinib, a medicine used to treat certain types of cancers
- tolvaptan (used to treat low levels of sodium in your blood or for kidney problems)
- halofantrine (used to treat malaria)
- warfarin (eg Marevan, Coumadin), a medicine used to stop blood clots
- phenytoin (Dilantin), a medicine used to treat epilepsy prednisone (used to treat inflammation or suppress the immune system)
- theophylline (eg. Nuelin), a medicine used to treat asthma
- certain benzodiazepines, medicines used as sedatives or to treat anxiety, such as midazolam (eg. Hypnovel) and triazolam (eg. Halcion)
- lemborexant (used to treat insomnia or sleeping difficulties)
- lurasidone (used to manage schizophrenia)
- hydrochlorothiazide, a medicine used to treat fluid problems and high blood pressure
- the contraceptive pill (birth control pill)
- carbamazepine (eg. Tegretol), a medicine used in the treatment of epilepsy and bipolar disorder
- NSAIDS such as naproxen, diclofenac and celecoxib (eg. Celebrex)
- Vitamin A
- Opioid pain killers such as alfentanil, fentanyl and methadone
- Losartan, a medicine used to treat high blood pressure
- antidepressants such as amitriptyline (eg. Endep) and nortriptyline.
Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines, vitamins or supplements you are taking and if these affect DIZOLE.
4. How do I use DIZOLE?
How much to take
Adults
- The dose will depend on your infection and how you respond to DIZOLE. It usually ranges from 50 to 400 mg once daily.
Children
- The dose for a child will depend on body weight and usually ranges from 3 mg to 12 mg per kilogram of body weight. In very young children (below 4 weeks of age), DIZOLE is usually given every second or third day.
However, depending on how serious the infection is, and how you react to the medicine, your doctor may ask you to take a different dose.
People with kidney problems may require smaller doses.
- Follow the instructions provided and use DIZOLE until your doctor tells you to stop.
When to take DIZOLE
- DIZOLE should be used about the same time each day.
- Taking it at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will also help you remember when to take it.
- DIZOLE can be taken with or without food.
How to take DIZOLE
- Swallow the capsules whole with a glass of water.
- Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully.
- They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
- If you do not understand the instructions on the pack, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How long to take it for?
- Continue taking DIZOLE for as long as your doctor tells you.
- The length of time you take DIZOLE will depend on the sort of infection you have.
- Patients with a weakened immune system or those with difficult infections may need long-term treatment to prevent the infection from returning.
- Do not stop taking DIZOLE because you are feeling better.
- If you do not complete the full course prescribed by your doctor, the infection may not clear completely, or your symptoms may return.
If you forget to use DIZOLE
DIZOLE should be used regularly at the same time each day. If you miss your dose at the usual time, please see the following instructions.
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose you missed. This may increase the chance of you getting an unwanted side effect.
Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember, and then go back to taking it as you would normally.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you use too much DIZOLE
If you think that you have used too much DIZOLE, you may need urgent medical attention.
You should immediately:
- phone the Poisons Information Centre
(Australia telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or - contact your doctor, or
- go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
5. What should I know while using DIZOLE?
Things you should do
- If you are about to be started on any new medicine, tell your doctor or pharmacist that you are taking DIZOLE.
- If you are a woman of child-bearing age, you should avoid becoming pregnant while taking DIZOLE. Talk to your doctor about the need for an additional method of contraception while being given DIZOLE. If you become pregnant while taking DIZOLE, tell your doctor immediately. This medicine is not recommended for use in pregnancy.
- If the symptoms of your infection do not improve within a few days or if they become worse, tell your doctor.
- Follow your doctor's advice if regular checks on your liver are recommended. In rare cases, DIZOLE may affect the liver and may need to be stopped.
- If you suffer from HIV or have a weakened immune system and develop a rash while taking DIZOLE, tell your doctor immediately. If this rash worsens, DIZOLE may need to be stopped.
- Keep all your doctor's appointments so that your progress can be checked.
- Remind any doctor, dentist or pharmacist you visit that you are using DIZOLE.
Things you should not do
- Do not start treatment if you have ever had an allergic reaction to any medicine containing fluconazole, any of the ingredients listed at the end of this CMI.
- Do not take DIZOLE to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
- Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
- Do not stop taking your medicine or change the dosage without checking with your doctor.
- If you do not complete the full course prescribed by your doctor, all of the organisms causing your infection may not be killed. These organisms may continue to grow and multiply so that your infection may not clear completely or may come back.
Driving or using machines
Be careful before you drive or use any machines or tools until you know how DIZOLE affects you.
Be careful when driving vehicles or operating machinery as occasional dizziness or seizures may occur.
Drinking alcohol
Tell your doctor if you drink alcohol.
Looking after your medicine
- Keep your capsules in the pack until it is time to take them.
- If you take the capsules out of the pack they may not keep well.
- Keep your capsules in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
- Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
- A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Follow the instructions in the carton on how to take care of your medicine properly.
Store it in a cool dry place away from moisture, heat or sunlight; for example, do not store it:
- in the bathroom or near a sink, or
- in the car or on window sills.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date, take it to any pharmacy for safe disposal.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date.
6. Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. This medicine helps most people with fungal and yeast infections, but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people. If you do experience any side effects, most of them are minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any further questions about side effects.
Less serious side effects
| Less serious side effects | What to do |
* These side effects may show up when you have a blood test. | Speak to your doctor if you have any of these less serious side effects and they worry you. |
Serious side effects
| Serious side effects | What to do |
Allergy or reaction related:
Skin changes:
Changes to urine:
Signs of frequent or worrying infections such as:
Other:
| Call your doctor straight away, or go straight to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects. |
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that may be making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed here may occur in some people.
Reporting side effects
After you have received medical advice for any side effects you experience, you can report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration online at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you decide to stop taking any of your medicines.
7. Product details
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What DIZOLE contains
| Active ingredient (main ingredient) |
|
| Other ingredients (inactive ingredients) |
|
| Potential allergens | Sulfites, phenylalanine, and sugars as lactose |
Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of these ingredients.
What DIZOLE looks like
DIZOLE capsules are available in 3 different strengths:
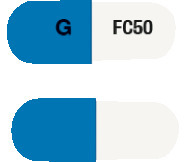
DIZOLE 50 is a hard gelatin capsule with one half white and the other half dark blue. The white half has "FC 50" and the dark blue half has "G" printed in black. Each pack contains 28 capsules. (AUST R 162640).
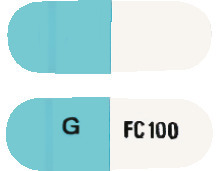
DIZOLE 100 is a hard gelatin capsule with one half white and the other half blue. The white half has "FC 100" and the blue half has "G" printed in black. Each pack contains 28 capsules. (AUST R 159620).
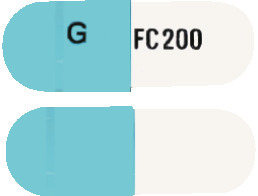
DIZOLE 200 is a hard gelatin capsule with one half white and the other half blue. The white half has "FC 200" and the blue half has "G" printed in black. Each pack contains 28 capsules. (AUST R 132789).
Who distributes DIZOLE
Alphapharm Pty Ltd trading as Viatris
Level 1, 30 The Bond
30-34 Hickson Road
Millers Point NSW 2000
www.viatris.com.au
Phone: 1800 274 276
This leaflet was prepared in November 2023.
DIZOLE® is a Viatris company trade mark
DIZOLE_cmi\Nov23/00
Published by MIMS January 2024




 The major route of excretion is renal, with approximately 80% of the administered dose appearing in the urine as unchanged drug. About 11% of the dose is excreted in the urine as metabolites. The pharmacokinetics of fluconazole is markedly affected by reduction in renal function. There is an inverse relationship between the elimination half-life and creatinine clearance. The dose of fluconazole may need to be reduced in patients with impaired renal function (see Section 4.2 Dose and Method of Administration). A 3 hour haemodialysis session reduces plasma concentration by about 50%.
The major route of excretion is renal, with approximately 80% of the administered dose appearing in the urine as unchanged drug. About 11% of the dose is excreted in the urine as metabolites. The pharmacokinetics of fluconazole is markedly affected by reduction in renal function. There is an inverse relationship between the elimination half-life and creatinine clearance. The dose of fluconazole may need to be reduced in patients with impaired renal function (see Section 4.2 Dose and Method of Administration). A 3 hour haemodialysis session reduces plasma concentration by about 50%. Clearance corrected for bodyweight was not affected by age in these studies. Mean body clearance in adults is reported to be 0.23 mL/minute/kg.
Clearance corrected for bodyweight was not affected by age in these studies. Mean body clearance in adults is reported to be 0.23 mL/minute/kg.
