What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about RALOVERA. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking RALOVERA against the benefits it is expected to have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What RALOVERA is used for
RALOVERA is a progestogen that comes from progesterone, a natural sex hormone. RALOVERA works in a similar way to progesterone.
RALOVERA is used to treat:
- endometriosis - a condition in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (womb) grows outside the uterus, causing pain and bleeding. RALOVERA helps to stop the growth of this tissue
- secondary amenorrhoea (a lack of menstrual periods not due to pregnancy). RALOVERA, with or without an estrogen, helps to re-establish a regular menstrual cycle
- abnormal bleeding from the uterus, when the lining of the uterus breaks down during the menstrual cycle rather than at the end, resulting in vaginal spotting or bleeding. RALOVERA helps to re-establish a regular menstrual cycle
- certain types of cancer including cancer of the breast, kidney and endometrium
- RALOVERA, in combination with an estrogen containing medicine, is used to relieve symptoms of menopause in women with an intact uterus. This is called hormone replacement therapy (HRT). RALOVERA is used to protect the lining of the uterus while the estrogens relieve the symptoms of menopause. RALOVERA is not suitable as a HRT treatment in women who have undergone a hysterectomy.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why RALOVERA has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
Before you take RALOVERA
When you must not take it
Do not take RALOVERA if you have an allergy to medroxyprogesterone acetate or any of the ingredients in RALOVERA listed at the end of this leaflet.
Do not take RALOVERA if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions:
- a stroke, blood clots or pulmonary embolism
- severe liver disease
- unusual or irregular vaginal bleeding or blood in your urine that has not been diagnosed by your doctor
- bleeding or discharge from your nipples
- breast cancer or breast lumps not diagnosed by your doctor
- a missed miscarriage
- uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Do not take RALOVERA if you are pregnant or suspect you may be pregnant. RALOVERA may affect your developing baby if you take it during pregnancy.
Do not take RALOVERA after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
If you are not sure whether you should start taking RALOVERA, contact your doctor.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Before prescribing RALOVERA for you, your doctor may conduct a physical examination which may include breast examinations or a mammogram and a PAP smear.
Tell your doctor if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions:
- heart problems
- kidney problems
- migraine
- unusual or irregular vaginal bleeding
- genital or breast cancer
- epilepsy
- asthma
- diabetes
- depression.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell him/her before you start taking RALOVERA.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including medicines you buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may interfere with RALOVERA. This includes aminoglutethimide, a medicine used to treat breast cancer. This medicine may affect how well RALOVERA works. You may need different amounts of your medicine or you may need to take different medicines. Your doctor will advise you.
Your doctor or pharmacist may have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking RALOVERA.
How to take RALOVERA
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the label or in this leaflet, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How much to take
Your doctor will tell you how much RALOVERA to take. This will vary depending on the condition for which you are being treated. RALOVERA should be used at the lowest effective dose to treat your condition.
Your doctor may tell you to take RALOVERA every day or in repeating cycles with a break in between.
How to take RALOVERA
Swallow the tablets whole with a full glass of water.
When to take RALOVERA
Take RALOVERA at about the same time each day. Taking it at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will also help you remember when to take it.
How long to take it
Continue taking your medicine for as long as your doctor tells you. Your doctor will prescribe RALOVERA for the shortest duration necessary to effectively treat your condition.
If you forget to take RALOVERA
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to.
Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember, and then go back to taking RALOVERA as you would normally.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed. This may increase the chance of you getting an unwanted side effect.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26), or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital if you think you or anyone else may have taken too much RALOVERA. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need medical attention.
While you are taking RALOVERA
Things you must do
Take RALOVERA exactly as your doctor has prescribed.
Tell your doctor if you think you may have become pregnant during treatment.
RALOVERA should not be used during pregnancy.
Tell your doctor immediately if you have sudden partial or complete loss of vision or sudden onset of double vision or migraine. You will need to be examined and may need to stop taking your medicine.
Tell all doctors and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking RALOVERA.
If you are about to start taking any new medicines, tell your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking RALOVERA.
If you are going to have any laboratory tests, tell your doctor that you are taking RALOVERA. RALOVERA may interfere with the results of some tests.
Tell your doctor if you feel that RALOVERA is not helping your condition.
Visit your doctor regularly. Your doctor needs to check your progress and see whether you need to keep taking RALOVERA.
Regularly check your breasts for any lumps and have regular professional breast examinations and mammograms, as recommended by your doctor.
If you are taking RALOVERA for prolonged periods, your doctor may also need to evaluate your bone mineral density (BMD). If you use RALOVERA as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for 5 or more years, your doctor will need to physically check your pelvic organs and conduct blood tests, to rule out the risk of developing ovarian cancer.
The use of RALOVERA may result in a decrease in the amount of calcium in your bones. This could increase your risk of developing brittle bones (osteoporosis), which can lead to bone breakages in later life. This effect can increase with long term use of RALOVERA. The amount of calcium in your bones will start to increase again once you stop treatment with RALOVERA. The time to recovery depends on duration of use. Some women may only partially recover the amount of calcium in their bone.
Tell your doctor if, for any reason, you have not taken RALOVERA exactly as prescribed.
Always discuss with your doctor any problems or difficulties during or after taking RALOVERA.
Things you must not do
Do not change your dose or stop taking RALOVERA without first checking with your doctor.
Do not take RALOVERA to treat other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not give RALOVERA to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Things to be careful of
RALOVERA generally does not cause any problems with your ability to drive a car or operate machinery. However, RALOVERA may cause dizziness, drowsiness or fatigue in some people.
Make sure you know how you react to RALOVERA before driving a car or operating machinery.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while taking or soon after you are finished taking RALOVERA.
RALOVERA helps most people for whom it is prescribed but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people. All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
If you are over 65 years of age you may have an increased chance of getting some side effects.
The use of an estrogen at the same time as RALOVERA may also increase the risk of side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and it worries you:
- nervousness or difficulty concentrating
- difficulty sleeping or increased sleepiness, drowsiness or fatigue
- depression or excitation
- dizziness
- headache
- skin conditions, such as hives, itching, rash or acne
- unusual hair loss or hair thinning or increased hairiness
- sweating
- irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting or unusual changes in vaginal secretions
- increased heart rate
- lack of menstrual periods
- nausea or vomiting
- constipation or diarrhoea
- dry mouth, increased thirst
- frequently urinating
- breast tenderness
- unusual secretion of breast milk
- changes in sexual drive
- fever
- weight increases or decreases
- changes in appetite
- muscle spasms
- leg cramps
- fluid retention
- impotence (mainly in cancer treated patients).
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if you notice the following:
- confusion or memory loss
- lumps or change in your breasts
- yellowing of the skin or eyes.
Although these side effects are not common, they may require further medical assessment for serious conditions, such as dementia or breast cancer.
Tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital if any of the following happen:
- painful swelling in the arms or legs
- swollen or tender veins
- chest pain or shortness of breath
- severe headaches or changes in speech or vision
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body, shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing.
- changes in metabolism resulting in the loss of body fat in certain areas of your body such as your face.
- hand tremors, swelling, cramps in calves at night.
- yellowing of the skin and/or eyes
The above list includes side effects that may indicate serious conditions that require urgent medical attention or hospitalisation, such as blood clots, heart attack, stroke or severe allergic reactions. Such side effects are not common.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some patients.
Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Some side effects (such as changes in blood pressure) can only be found when your doctor does tests from time to time to check your progress.
After taking RALOVERA
Storage
Keep your tablets in the pack until it is time to take them. If you take the tablets out of the pack they may not keep well.
Keep RALOVERA in a cool, dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C.
Do not store RALOVERA, or any other medicine, in a bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car or on windowsills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep your RALOVERA tablets where children cannot reach them. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking RALOVERA, or it has passed its expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any tablets left over.
Product description
What it looks like
RALOVERA tablets are available in 5 mg and 10 mg strengths.
RALOVERA 5 mg tablets are pale blue, round and flat, scored and marked "286" on one side and "U" on the other. The 5 mg tablets are available in blister packs of 56 tablets.
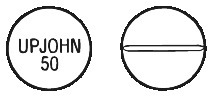
RALOVERA 10 mg tablets are white, round and convex, scored on one side and marked "UPJOHN 50" on the other. The 10 mg tablets are available in blister packs of 30 and bottles of 100.
Ingredients
Active ingredients
The active ingredient in RALOVERA tablets is medroxyprogesterone acetate.
Other ingredients
RALOVERA tablets also contain:
- lactose
- sucrose
- maize-starch
- liquid paraffin
- purified talc
- calcium stearate
- indigo carmine (5 mg).
RALOVERA 10 mg tablets do not contain colouring agents.
Supplier
RALOVERA tablets are supplied in Australia by:
Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd
Sydney NSW
Toll free number: 1800 675 229
www.pfizer.com.au
Australian Registration Numbers
5 mg blister: AUST R 46531.
10 mg blister: AUST R 46532.
10 mg bottle: AUST R 46534.
This leaflet was revised in April 2020.
Published by MIMS June 2020


 The reported risk at 10 years or more after discontinuation of treatment was not increased when therapy was taken for less than 5 years. See Table 2.
The reported risk at 10 years or more after discontinuation of treatment was not increased when therapy was taken for less than 5 years. See Table 2. In current users, the increased risk of breast cancer in women taking combined estrogen-progestin MHT becomes apparent after about 1-4 years. See Table 3.
In current users, the increased risk of breast cancer in women taking combined estrogen-progestin MHT becomes apparent after about 1-4 years. See Table 3.

