What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about bosentan.
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you using this medicine against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What this medicine is used for
Bosentan is used to treat high blood pressure in the blood vessels between the heart and the lungs. This condition is called pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Bosentan belongs to a group of medicines called endothelin antagonists.
How it works
Bosentan acts to reduce abnormally high blood pressure by widening the blood vessels between the heart and lungs.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed this medicine for another reason.
This medicine is available only with a doctor's prescription.
This medicine is not addictive.
There is limited experience with the use of this medicine in children.
Before you take this medicine
When you must not take it
Do not take this medicine if you are:
- pregnant or intend to become pregnant. You must stop taking this medicine at least 3 months before trying to become pregnant.
It is known that this medicine causes harm to the developing baby if you take it during pregnancy and in the three months before becoming pregnant. - breastfeeding:
Tell your doctor immediately if you are breastfeeding. You are advised to stop breastfeeding if this medicine is prescribed for you because it has been reported that this drug passes into the milk in a women who was taking this medicine. - if you are taking ciclosporin A (a medicine used after a transplant or to treat psoriasis)
- being treated with glibenclamide (a medicine used for diabetes).
Do not take this medicine if you have an allergic to or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
Do not take this medicine if you have a moderate to severe liver disorder.
Do not take this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
Before you start to take it
Bosentan may harm sperm. All men should use effective birth control while taking this medicine and for 3 months after they stop taking it.
If sexually active, you must use a hormonal and barrier method of contraception. This medicine may reduce the effectiveness of hormone contraceptives such as the pill, hormone patches, implants or injections. It is important to use other contraceptives, like condoms or an intrauterine device (IUD).
Your doctor will advise you about using reliable contraceptives before taking this medicine.
You must have a negative pregnancy test at the time of starting treatment, and have a pregnancy test every month while you are taking this medicine if you are sexually active. Your doctor will need evidence that you are not pregnant before prescribing bosentan.
Tell your doctor if:
- you are a woman of childbearing potential and not using reliable contraceptive methods. You must have a negative pregnancy test before beginning treatment. The test should be performed on the second day of a normal menstrual period or 11 days after the last unprotected sexual intercourse, whichever is later. Your doctor will advise you about using reliable contraception before taking or whilst taking this medicine.
Hormonal contraception on its own is not a reliable option because this medicine may make this method ineffective in preventing pregnancy. Hormonal contraceptives include ones you take orally (the pill), patches you put on your skin, ones that are injected and implants. You should ALWAYS use additional methods of contraception, such as condoms and IUDs, and not rely only on hormonal contraception. You should have a pregnancy test every month while you are taking this medicine. You must stop taking this medicine for at least 3 months prior to becoming pregnant.
- you are breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed.
It is not known whether bosentan passes into breast milk.
- you have allergies to:
- any other medicines
- any other substances such as food, preservatives or dyes.
- you have or have had any of the following medical conditions, especially the following:
- pulmonary arterial hypertension or lung disease /condition
- anaemia
- hypotension
- liver or kidney disorders
- heart failure or disease
- HIV infection
Tell your doctor if you are planning to have surgery, dental treatment or an anaesthetic.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you start taking bosentan.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may also interfere with bosentan. These include:
- hormonal contraceptives (oral, injectable, transdermal and implantable)
- simvastatin, used for lowering blood fats
- medicines for diabetes such as glibenclamide and tolbutamide.
- medicines used for fungal infections (e.g. ketoconazole, fluconazole and voriconazole)
- medicines for bacterial infections (e.g. rifampicin)
- medicines to prevent organ transplantation rejection (e.g. ciclosporin A, tacrolimus, sirolimus)
- medicines for rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis/dermatitis
- lopinavir and ritonavir or other ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors and nevirapine (used to treat HIV infections);
- warfarin, used to prevent blood clots
- digoxin, used to treat heart rhythm disorders
- sildenafil or tadalafil used to treat erectile dysfunction or pulmonary arterial hypertension
- phenytoin, carbamazepine or phenobarbital (medicines for seizures)
- nimodipine, a type of medication used to treat narrow blood vessels in the brain.
- St John's Wort
These medicines may be affected by this medicine or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines.
Your doctor and pharmacist have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
Other medicines not listed above may also interact with bosentan.
How to take this medicine
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor carefully. They may differ to the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the bottle, ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How much to take
Your doctor will tell you how much of this medicine you should take. This will depend on your condition and whether you are taking any other medicines.
Adults
The usual starting dose is one 62.5 mg tablet taken twice daily.
Depending on how you respond to the medicine, your doctor may increase the dosage after four weeks to one 125mg tablet twice daily.
Patients with low body weight
If you have body weight less than 40 kg but are over 12 years old, your doctor may advise you take 62.5 mg tablet twice daily.
Children aged 3 years and over
The dose will determined by your doctor depending on the weight of the child.
Talk to your doctor if you do not think the medicine is working or you think it is working too well. Your doctor may need to change the dose you are taking.
How to take it
Swallow the tablet whole with a full glass of water.
When to take it
Take one tablet in the morning and one tablet in the evening, at about the same time each day. It can be taken with or without food. Taking it at the same time each day will have the best effect and will also help you remember when to take it.
It does not matter if you take this medicine before or after food.
How long to take it for
Continue taking your medicine for as long as your doctor tells you.
Stopping your treatment may lead to a worsening of your symptoms. Your doctor may tell you to reduce the dose over a few days before stopping completely.
This medicine helps to control your condition but does not cure it. It is important to keep taking your medicine even if you feel well.
Make sure you have enough medicine to last over weekends and holidays.
If you forget to take it
If it is almost time to take your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to.
Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember and then go back to taking your medicine as you would normally.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose you missed. This may increase the chance of you experiencing side effects.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints to help you remember.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much of this medicine.
Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are taking this medicine
Things you must do
It is very important that you have a liver function blood test before you start treatment and every month after that. Bosentan can cause liver damage if it is not found early. As this side effect may not cause symptoms at first, only a blood test can show that you have early liver damage. Regular blood tests let your doctor change or stop your therapy before there is permanent damage.
You should have a blood test for anaemia after 1 and 3 months and then every 3 months for the rest of your treatment.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor and pharmacist that you are taking this medicine.
If you are about to have any blood tests, tell the doctor that you are taking this medicine.
If you are going to have surgery, tell the surgeon and anaesthetist that you are taking this medicine. It may affect other medicines used during surgery.
Tell any other doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you take this medicine.
Things you must not do
Do not become pregnant whilst taking this medicine. You must have a pregnancy test every month while you are taking this medicine.
If there is any delay in getting period or any other reason to suspect pregnancy, you must tell your doctor immediately for pregnancy testing. Bosentan may harm unborn babies.
You doctor will need evidence that you are not pregnant before prescribing the medicine again.
Do not give this medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not take your medicine to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not stop taking your medicine or change your dosage without first checking with your doctor. Stopping your treatment may lead to worsening of your symptoms. Your doctor may tell you to reduce the dose over a few days before stopping completely.
Things to be careful of
Be careful when driving or operating machinery until you know how this medicine affects you. This medicine may cause tiredness in some people. Feel dizzy or that your vision is blurred whilst taking this medicine. If you have any of these symptoms, do not drive, operate machinery or do anything else that could be dangerous.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking bosentan.
Bosentan helps most people with pulmonary hypertension but may have unwanted side effects in a few people. All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following:
- headache
- respiratory tract infection
- dizziness or fainting
- anaemia
- abnormal liver function test or liver disorders
- inflamed throat and irritated nasal passages
- joint pain
- flushing (hot flushes)
- swelling of ankle, leg and signs of fluid retention
- low blood pressure
- blood disorders
- fast heart beat
- tiredness
- blurred vision
- hypersensitivity reactions including itching, rash, skin inflammation, skin redness
- blocked or runny nose
- heartburn or acid reflux
- diarrhoea
- nosebleed
- body ache and pain
- worsening of existing lung disease
The above list includes some side effects that may require medical attention.
If any of the following happen, stop taking your medicine and contact your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- anaphylaxis and/ or swelling most commonly around the eyes, lips, tongue, throat
- shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty in breathing.
- nausea or vomiting
- fever
- unusual tiredness
- stomach pain
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes (jaundice).
- dark-coloured urine
- chest pain
The above list includes very serious side effects and you may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
Serious side effects are uncommon.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell. Other side effects not listed above may occur in some patients.
Storage and disposal
Storage
Keep your medicine in its original packaging until it is time to take it. If you take your medicine out of its bottle it may not keep well.
Keep your medicine in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Do not store your medicine, or any other medicine, in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it on a window sill or in the car. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep this medicine where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking this medicine or the expiry date has passed, ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over.
Product description
What it looks like
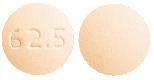
62.5 mg film coated tablets are light peach to peach coloured, round shaped, biconvex and debossed with '62.5' on one side and plain on the other side.
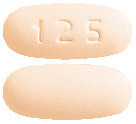
125 mg film coated tablets are light peach to peach coloured, oval shaped, biconvex and debossed with '125' on one side and plain on the other side.
Ingredients
Each tablet contains 62.5 mg or 125 mg bosentan (as monohydrate) as the active ingredient.
It also contains the following inactive ingredients:
- maize starch
- pregelatinised maize starch
- sodium starch glycollate type A
- povidone
- glycerol dibehenate
- magnesium stearate
Film coating is OPADRY complete film coating system 21K520019 Yellow, which contains:
- hypromellose
- triacetin
- purified talc
- titanium dioxide
- iron oxide yellow
- iron oxide red
- ethylcellulose
This medicine does not contain gluten, lactose, sucrose, tartrazine and other azo dyes.
Australian Registration Numbers
Bosentan APO 62.5 mg (bottle of 60 tablets) AUST R 257754.
Bosentan APO 125 mg (bottle of 60 tablets) AUST R 257734.
Sponsor
Arrotex Pharmaceutical Pty Ltd
15-17 Chapel Street
Cremorne 3121
www.arrotex.com.au
This leaflet was prepared in March 2024.
Published by MIMS April 2024


 Additional adverse events occurring in the subset of patients treated for PAH, in at least 3% of patients on bosentan and more frequently than on placebo are presented in Table 3.
Additional adverse events occurring in the subset of patients treated for PAH, in at least 3% of patients on bosentan and more frequently than on placebo are presented in Table 3. Treatment with bosentan has been associated with dose-dependent elevations in liver aminotransferases and decreases in haemoglobin concentration (see Section 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use).
Treatment with bosentan has been associated with dose-dependent elevations in liver aminotransferases and decreases in haemoglobin concentration (see Section 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use). In the post-marketing period, rare cases of unexplained hepatic cirrhosis were reported after prolonged therapy with bosentan in patients with multiple co-morbidities and drug therapies. There have also been rare reports of liver failure. These cases reinforce the importance of strict adherence to the monthly schedule for monitoring of liver function for the duration of treatment with bosentan.
In the post-marketing period, rare cases of unexplained hepatic cirrhosis were reported after prolonged therapy with bosentan in patients with multiple co-morbidities and drug therapies. There have also been rare reports of liver failure. These cases reinforce the importance of strict adherence to the monthly schedule for monitoring of liver function for the duration of treatment with bosentan. In both trials, treatment with bosentan resulted in a significant increase in exercise capacity. The improvement in walk distance was apparent after 1 month of treatment (with 62.5 mg twice daily) and fully developed by about 2 months of treatment (Figure 1). It was maintained for up to 7 months of double-blind treatment. The placebo-subtracted mean increase in walking distance was somewhat greater with 250 mg twice daily (54 m) than with 125 mg twice daily (35 m). However, the higher dose is not recommended because of the potential for increased liver injury (see Section 4.2 Dose and Method of Administration).
In both trials, treatment with bosentan resulted in a significant increase in exercise capacity. The improvement in walk distance was apparent after 1 month of treatment (with 62.5 mg twice daily) and fully developed by about 2 months of treatment (Figure 1). It was maintained for up to 7 months of double-blind treatment. The placebo-subtracted mean increase in walking distance was somewhat greater with 250 mg twice daily (54 m) than with 125 mg twice daily (35 m). However, the higher dose is not recommended because of the potential for increased liver injury (see Section 4.2 Dose and Method of Administration). There were no apparent differences in treatment effects on walk distance among subgroups analysed by demographic factors, baseline disease severity, or disease aetiology, but the studies had little power to detect such differences.
There were no apparent differences in treatment effects on walk distance among subgroups analysed by demographic factors, baseline disease severity, or disease aetiology, but the studies had little power to detect such differences.
 There are limited data available on the minimum effective dose, dose response, and the clinically useful dose-range for bosentan. There are no studies to demonstrate beneficial effects on survival of treatment with bosentan. However, long-term vital status was recorded for all 235 patients who were treated with bosentan in the two pivotal placebo-controlled trials (AC-052-351 and AC-052-352) and/or their two uncontrolled, open-label extensions. The mean duration of exposure to bosentan was 1.9 years ± 0.7 years; [min: 0.1; max: 3.3 years] and patients were observed for a mean of 2.0 ± 0.6 years. The majority of patients were diagnosed as PPH (72%) and were in WHO functional class III (84%). In this total population, Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival were 93% and 84% after 1 and 2 years after the start of treatment with bosentan, respectively. Survival estimates were lower in the subgroup of patients with PAH secondary to systemic sclerosis. The estimates may have been influenced by the initiation of epoprostenol treatment in 43/235 patients.
There are limited data available on the minimum effective dose, dose response, and the clinically useful dose-range for bosentan. There are no studies to demonstrate beneficial effects on survival of treatment with bosentan. However, long-term vital status was recorded for all 235 patients who were treated with bosentan in the two pivotal placebo-controlled trials (AC-052-351 and AC-052-352) and/or their two uncontrolled, open-label extensions. The mean duration of exposure to bosentan was 1.9 years ± 0.7 years; [min: 0.1; max: 3.3 years] and patients were observed for a mean of 2.0 ± 0.6 years. The majority of patients were diagnosed as PPH (72%) and were in WHO functional class III (84%). In this total population, Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival were 93% and 84% after 1 and 2 years after the start of treatment with bosentan, respectively. Survival estimates were lower in the subgroup of patients with PAH secondary to systemic sclerosis. The estimates may have been influenced by the initiation of epoprostenol treatment in 43/235 patients. Patients with WHO functional class II PAH, on average, have only moderately impaired 6MWT and may therefore have a limited response range for improvement in this parameter. This could partly explain the lack of statistical significance for the 6MWT endpoint. However, there was a clear association between an absence of deterioration from baseline in 6MWT and stable WHO functional class in the EARLY population. No patient in the bosentan group who at least maintained baseline 6MWT had deterioration in functional class.
Patients with WHO functional class II PAH, on average, have only moderately impaired 6MWT and may therefore have a limited response range for improvement in this parameter. This could partly explain the lack of statistical significance for the 6MWT endpoint. However, there was a clear association between an absence of deterioration from baseline in 6MWT and stable WHO functional class in the EARLY population. No patient in the bosentan group who at least maintained baseline 6MWT had deterioration in functional class. The EARLY study was designed and powered to evaluate the efficacy of bosentan in the patient population as a whole and was not powered to show statistical significance for each aetiological sub-group. No criteria to determine aetiological subgroup numbers or specific claims of a beneficial effect by subgroup were pre-specified. Subgroup analyses of treatment effects according to PAH aetiology were performed in the EARLY trial with the objective being to support absence of heterogeneity in treatment response between subgroups. For both co-primary endpoints, the confidence intervals for treatment effects were overlapping between the major aetiological subgroups. The inclusion criteria for EARLY permitted recruitment of any patient with PAH determined to be idiopathic/familial or secondary to congenital heart defect, or connective tissue disease and other predefined aetiologies. For patients with congenital heart disease the defect had to be isolated and restrictive with no reverse shunt (atrial septum defect (ASD) < 2 cm, ventricular septum defect (VSD) < 1 cm or patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)). The population eventually enrolled reasonably reflected the relative incidences of PAH aetiologies seen in the real-world setting. Consequently, there was more data available for analysis in the most prevalent aetiological subgroups of idiopathic/familial PAH compared with the other subgroups.
The EARLY study was designed and powered to evaluate the efficacy of bosentan in the patient population as a whole and was not powered to show statistical significance for each aetiological sub-group. No criteria to determine aetiological subgroup numbers or specific claims of a beneficial effect by subgroup were pre-specified. Subgroup analyses of treatment effects according to PAH aetiology were performed in the EARLY trial with the objective being to support absence of heterogeneity in treatment response between subgroups. For both co-primary endpoints, the confidence intervals for treatment effects were overlapping between the major aetiological subgroups. The inclusion criteria for EARLY permitted recruitment of any patient with PAH determined to be idiopathic/familial or secondary to congenital heart defect, or connective tissue disease and other predefined aetiologies. For patients with congenital heart disease the defect had to be isolated and restrictive with no reverse shunt (atrial septum defect (ASD) < 2 cm, ventricular septum defect (VSD) < 1 cm or patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)). The population eventually enrolled reasonably reflected the relative incidences of PAH aetiologies seen in the real-world setting. Consequently, there was more data available for analysis in the most prevalent aetiological subgroups of idiopathic/familial PAH compared with the other subgroups. Chemical name: benzenesulphonamide, 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N-[6-(2hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2- methoxyphenoxy)[2,2'-bipyrimidin]-4-yl]-, monohydrate.
Chemical name: benzenesulphonamide, 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-N-[6-(2hydroxyethoxy)-5-(2- methoxyphenoxy)[2,2'-bipyrimidin]-4-yl]-, monohydrate.