What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about DIAMOX. It does not contain all of the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking DIAMOX against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any concerns about taking this medicine.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What DIAMOX is used for
DIAMOX is used to lower raised pressure in the eye and to treat the following forms of glaucoma:
- Chronic simple (open-angle) glaucoma
- Secondary glaucoma, where glaucoma has developed as a result of other eye disorders
- Acute angle-closure glaucoma before undergoing surgery.
Glaucoma is the name given to a group of eye diseases in which the optic nerve at the back of the eye is slowly destroyed. In most people this damage is caused by increased pressure in the eye. However, some people with glaucoma may have normal eye pressure.
Glaucoma is usually caused by a build up of fluid which flows into the eye. This build up occurs because the fluid drains out of your eye more slowly than it is being pumped in. Since new fluid continues to enter the eye, joining the fluid that is already there, the pressure continues to rise. This raised pressure may damage the back of the eye, resulting in gradual loss of sight. Damage can progress so slowly that the person is not aware of this gradual loss of sight. Sometimes even normal eye pressure is associated with damage to the back of the eye.
There are usually no symptoms of glaucoma. The only way of knowing is to have your eye pressure, optic nerve, and visual field checked by an eye specialist or optometrist. If glaucoma is not treated it can lead to serious problems. You may have no symptoms but eventually glaucoma can lead to total blindness. In fact, untreated glaucoma is one of the most common causes of blindness.
DIAMOX is used, either alone or in combination with other eye drops or medicines, to lower raised pressure within your eyes.
DIAMOX is also used to help treat some other conditions such as:
- Fluid retention due to congestive heart failure
- Fluid retention caused by other medicines
- Epilepsy in both adults and children
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why DIAMOX has been prescribed for you. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another purpose.
DIAMOX works by blocking an enzyme, which is responsible for fluid formation. In people with glaucoma, blocking this enzyme causes the pressure in the eye caused by fluid build up to fall. Blocking this enzyme also seems to slow down abnormal or excessive discharge from your nerves. This helps prevent fits in people with epilepsy.
It also acts as a diuretic. This gets rid of excess fluid in the body by increasing urine production. This action helps people with congestive heart failure or fluid retention caused by other medicines.
DIAMOX is not addictive.
This medicine is available only with a doctor’s prescription.
Before you take it
When you must not take it
Do not take DIAMOX if:
- you are allergic to:
- DIAMOX or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
- medicines called sulphonamides, which are a group of antibiotics used to treat bacterial infections, or sulphonamide related medicines
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction to DIAMOX or sulphonamides may include fever, rash and crystals in the urine.
- you have chronic noncongestive angle closure glaucoma.
- you have any of the following conditions:
- marked liver or kidney disease
If you have chronic liver disease and you take DIAMOX you are at risk of brain and nervous system damage. - problems with your adrenal glands
- unusual amounts of salt in the body
- low levels of sodium, potassium or bicarbonate in your blood
- Severe glaucoma due to peripheral anterior synechia or haemorrhagic glaucoma.
- you are pregnant.
DIAMOX should not be used in pregnancy, especially during the first trimester.
Do not use this medicine if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Do not use DIAMOX after the expiry date (EXP) printed on the pack. If you take it after the expiry date has passed, it may not work as well.
Before you take it
You must tell your doctor if:
- you have any allergies to:
- any other medicines
- any other substances, such as foods, preservatives or dyes
- you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of taking DIAMOX during pregnancy.
- you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed.
Your doctor will discuss the risks and benefits of taking DIAMOX when breastfeeding. This medicine has been found in low levels in breast milk.
- you have or have had any other medical conditions including:
- emphysema
- blockages in the lung
- diabetes or impaired glucose tolerance
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you take any DIAMOX.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including medicines that you buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines may reduce or increase the action of DIAMOX. Also, DIAMOX may reduce or increase the action of some other medicines. These include:
- aspirin
- phenytoin, primidone, medicines used to treat epilepsy
- medicines used to stop blood clotting
- medicines used for high blood sugar levels
- a group of medicines used to treat cancer called folic acid antagonists
- medicines used for high blood pressure
- medicines used to treat heart failure
- ciclosporin, a medicine used after an organ transplant to prevent rejection
- lithium, a medicine used to treat emotional disorders
- amphetamines (stimulants)
- other glaucoma medicines like DIAMOX
- antibiotics belonging to the methenamine class
- sodium bicarbonate, used to treat heartburn or to make your blood or urine less acidic
You may need to take different amounts of your medicine or you may need to take different medicines.
Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking DIAMOX.
How to take DIAMOX
How much to take
The dose of DIAMOX may be different for each person. Your doctor will decide the right dose for you.
The usual dose for chronic simple (open-angle) glaucoma is 250 mg (1 tablet) to 1 gram (4 tablets) per 24 hours. If the dose per 24 hours is greater than 250 mg, then the tablets are taken in divided doses.
For secondary glaucoma and for use before surgery in people with acute closed-angle glaucoma, the usual dose is 250 mg every 4 hours.
For epilepsy, the recommended dose for children is based on their bodyweight. Children take 8 – 30 mg per kilogram of bodyweight a day in divided doses. The total daily dose must not be greater than 750 mg per day. This equals three tablets a day.
For adults with epilepsy the usual dose is 250 mg (1 tablet) to 1 gram (4 tablets) daily in divided doses.
If you are taking DIAMOX with another medicine for your epilepsy, the starting dose for DIAMOX is usually 250 mg once daily in addition to your epilepsy medicine.
For congestive heart failure, the usual starting dose is 250 mg to 375 mg once daily in the morning.
For fluid retention caused by other drugs, the usual dose is 250 mg to 375 mg once daily for 1 to 2 days, alternating with a day of rest.
How to take it
Swallow DIAMOX with a glass of water.
This medicine may be taken with or without food.
When to take it
If you are taking DIAMOX in divided doses, take your tablets at evenly spaced time periods over a 24-hour period.
For congestive heart failure, take the medicine in the morning.
For congestive heart failure and drug-induced fluid retention, if your doctor prescribes two days therapy of DIAMOX, take your medicine on the first day, then no medicine the next day and then the second dose on the third day. DIAMOX gets rid of excess fluid best when given every other day over a three day period.
Follow your doctor’s dosing instructions if they are different from the instructions given in this leaflet.
How long to take it
For congestive heart failure and fluid retention caused by other medicines, do not take DIAMOX for longer than your doctor says. DIAMOX may not work as well if too many doses are given.
For glaucoma DIAMOX helps control your condition, but does not cure it. Therefore you must take your medicine every day. Continue taking the tablets for as long as your doctor tells you.
If you forget to take it
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to. Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember, and then go back to taking it as you would normally.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed.
If you are unsure about whether to take your next dose, speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering when to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or Poisons Information Centre on 131 126 for advice, or go to accident and emergency at your nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much DIAMOX. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. Make sure to report all other medicines or alcohol which has been taken. You may need urgent medical attention. Keep telephone numbers for these places handy.
While you are using it
Things you must do
Take DIAMOX exactly as your doctor has prescribed.
Tell all doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking DIAMOX.
If you become pregnant while you are taking this medicine, tell your doctor immediately.
Tell your doctor if you feel DIAMOX is not helping your condition.
Visit your doctor regularly. Your doctor needs to check your progress and see whether you need to keep taking DIAMOX.
Always discuss with your doctor any problems or difficulties during or after taking DIAMOX.
Tell your doctor if, for any reason, you have not taken your medicine exactly as prescribed. Otherwise your doctor may think that it was not effective and change your treatment unnecessarily.
Keep enough of this medicine to last weekends and holidays.
Things you must not do
Do not drive or operate machinery until you know how DIAMOX affects you. It may cause drowsiness or dizziness in some people and therefore may affect alertness. Make sure you know how you react to DIAMOX before you drive a car, operate machinery, or do anything else that could be dangerous if you are drowsy, dizzy or not alert.
Do not take DIAMOX for a longer time than your doctor has prescribed. For some conditions, DIAMOX should be taken for short periods only unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
Do not change your dose without first checking with your doctor.
Do not suddenly stop taking DIAMOX if you suffer from epilepsy. Stopping this medicine suddenly may make your epilepsy worse.
Do not use this medicine to treat any other complaints unless your doctor says to.
Do not give DIAMOX to anyone else, even if their symptoms seem similar to yours.
Things to be careful of
Be careful if you are elderly, unwell or taking other medicines. Some people may experience side effects such as drowsiness, confusion, and dizziness, which may increase the risk of a fall.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are using DIAMOX.
It helps most people with their condition, but it may have unwanted side effects in some people.
All medicines may have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- tingling or numbness of fingers, toes, hands, feet and face
- loss of appetite
- feeling extremely thirsty
- passing more urine than normal
- flushing
- headache
- dizziness
- tiredness
- irritability
These side effects are usually mild.
Less common or rare side effects include:
- drowsiness
- depression
- over-excitement
- confusion
- increased sensitivity of the skin to the sun
- fast breathing
- low potassium levels in the blood
- nausea/vomiting
- diarrhoea
- temporary shortsightedness
- itchy rash or hives
- blood in the urine
- sugar in the urine
- black tar-like stools
- liver problems
- fits
- paralysis where the muscles are limp and unable to move
- kidney disease including kidney stones
- crystals in the urine
- hearing disturbances such as ringing in the ears
- growth retardation in children
- weakness of the bones
- taste alteration
- low or high blood sugar levels
- unsteadiness when walking
- severe skin reactions such as blisters and bleeding from the lips, eyes, mouth, nose or genitals
Tell your doctor immediately or go to casualty at your nearest hospital if you notice any of the following:
- frequent infections such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers
- sudden signs of allergy such as rash, itching, hives, swelling of the face, lips or tongue and shortness of breath or wheezing
- signs of shock such as rapid, shallow breathing, cold, clammy skin, a rapid, weak pulse and dizziness or fainting
- bruising or bleeding more easily than normal
- tiredness, headaches, being short of breath when exercising, dizziness, looking pale and yellowing of the skin and/or eyes.
These are serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. Serious side effects are rare.
Deaths have occurred rarely due to severe adverse reactions to sulphonamides.
Other side effects not listed above may occur in some patients. Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell when you are taking, or soon after you have finished taking, DIAMOX.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you don’t understand anything in this list.
Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
After using it
Storage
Keep your tablets in their bottle until it is time to take them. If you take the tablets out of the bottle they may not keep well.
Keep DIAMOX in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C. Do not store it, or any other medicines, in a bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car or on window sills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking DIAMOX or the tablets have passed their expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any tablets left over.
Product description
What it looks like
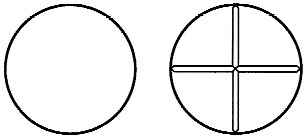
DIAMOX tablets are white, round, convex tablet, one side plain, the other side scored into quarters.
DIAMOX comes in a plastic bottle containing 100 tablets.
Ingredients
The active ingredient in DIAMOX is acetazolamide. Each tablet contains 250 mg acetazolamide.
DIAMOX tablets also contain the following inactive ingredients:
- sodium starch glycollate
- povidone
- calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate
- maize starch
- magnesium stearate
They do not contain gluten, lactose, sucrose, tartrazine or any other azo dyes.
Supplier
DIAMOX is supplied by:
Arrotex Pharmaceuticals Pty Ltd
15-17 Chapel Street
Cremorne VIC 3121
Australia
www.arrotex.com.au
Australian Registration Number:
DIAMOX 250 mg Tablets
AUST R 15204
This leaflet was revised May 2024
Published by MIMS July 2024

 C4H6N4O3S2.
C4H6N4O3S2.