What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Norgesic tablets. However it does not contain all the available information. Your doctor and pharmacist have more information about this medicine.
If you have any questions about Norgesic that are not answered by this leaflet, please ask your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of your taking Norgesic against the benefits before prescribing it for you.
If you are worried about taking this medicine please talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with your medicine as you may want to read it again.
What Norgesic is used for
The name of your medicine is Norgesic. It contains orphenadrine citrate and paracetamol.
Orphenadrine citrate is a skeletal muscle relaxant. It acts in the central nervous system to produce muscle relaxant effects. Paracetamol is used to treat or prevent pain and reduce fever.
Norgesic is used to treat tension headache and headaches caused by spasm of the muscles in the back of your head and neck.
It is also used to help relax certain muscles in your body and to relieve the pain and discomfort caused by sprains, strains or other injury to your muscles.
Your doctor may have prescribed Norgesic for another purpose.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why this medicine has been prescribed for you.
Before you take Norgesic
When you must not take it
Do not take Norgesic if you have had an allergic reaction to orphenadrine citrate, paracetamol or other similar medicines, or to any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Do not take Norgesic if you have any of the following:
- glaucoma (high pressure in the eye);
- intestinal blockage or oesophageal disease
- enlarged prostate or bladder obstruction;
- myasthenia gravis (a disease of the muscles causing drooping eyelids, double vision, difficulty in speaking and swallowing, and, sometimes, muscle weakness in the arms or legs).
Do not take Norgesic:
- after the expiry date on the pack;
- if the packaging shows signs of tampering.
- unless advised by your doctor
Do not give this medicine to a child under the age of 12 years. Safety and effectiveness in children younger than 12 years have not been established.
Before you start to take Norgesic
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if
- you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes;
- you have any heart problems;
- you have any liver or kidney problems;
- you have alcohol abuse problems.
- you are taking other Paracetamol containing products.
Norgesic is not recommended for use during pregnancy or lactation. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or breast feeding or intend to become pregnant or breastfeed. Your doctor or pharmacist will discuss the possible risks and benefits of using Norgesic during pregnancy.
If you are not sure whether to start taking this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food store.
Some medicines when taken with Norgesic may interfere with each other. These include:
- anticholinergics (medicines used to relieve stomach cramps or spasms).
- medicines used to treat depression.
- other central nervous system depressant drugs, including alcohol. Examples of CNS depressants are antihistamines or medicines for hayfever, other allergies or colds; sedatives or tranquilizers; narcotic analgesics (eg. dextropropoxyphene); barbiturates; medicines for seizures; anaesthetics, including some dental anaesthetics; and other muscle relaxants.
- medicines used to treat epilepsy or fits.
- medicines used to prevent blood clots.
- medicines which affect gastric emptying eg metoclopramide, propantheline.
- chloramphenicol, which is an antibiotic
You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines. Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking Norgesic.
How to take Norgesic
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor or pharmacist carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the pack ask your doctor or pharmacist for help.
How much to take
The usual dose of Norgesic in adults is two tablets three times a day. Your doctor will prescribe the correct dose for you.
Take Norgesic tablets only as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. Do not change the dose unless your doctor tells you to do so.
If you forget to take your medicine
If you miss a dose of this medicine and remember within an hour or so of the missed dose, take it right away. If you do not remember until later, skip the missed dose and go back to taking it as you would normally.
Do not take double doses.
If you take too much (overdose)
Overdose with paracetamol-containing medicines can lead to liver damage.
Do not take more than the recommended dose unless your doctor tells you to.
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (in Australia call 13 11 26; in New Zealand call toll free 0800 POISON or 0800 764 766) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much Norgesic. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
Symptoms of an overdose include abdominal pain; vomiting; increased sweating; severe drowsiness; difficulty breathing; cyanosis; excitement; confusion; severe confusion leading to coma; convulsions; fast heart rate; dilated pupils and difficulty passing urine.
While you are taking Norgesic
Things you must do
Tell all doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking Norgesic.
Tell your doctor immediately if you become pregnant while taking this medicine.
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how the medicine affects you. Norgesic may cause some people to have blurred vision or to become drowsy, dizzy, light-headed, faint or less alert than they are normally. It may also cause muscle weakness in some people. If you have any of these symptoms do not drive or operate machinery or do anything else that could be dangerous.
Norgesic may cause dryness of the mouth. For temporary relief use sugarless gum or sweets, melt some ice in your mouth or use a saliva substitute.
If dry mouth continues for more than 2 weeks speak to your dentist. Continued dryness of the mouth can increase the chance of dental disease, including tooth decay, gum disease and fungal infections.
Things you must not do
Norgesic is a prescription medicine and has been prescribed for you only.
Do not give it to anyone else even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not take Norgesic to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Side Effects
All medicines can cause unwanted side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not.
Speak to your doctor if any of the following side effects occur:
Less common: decreased urination; eye pain; fainting; fast or pounding heartbeat.
Rare: hallucinations; shortness of breath; troubled breathing; tightness in chest and/or wheezing; skin rash; sores, ulcers or white spots on lips or in mouth; swollen and/or painful glands; unusual bruising or bleeding; unusual tiredness or weakness.
The following side effects usually do not need medical attention and may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine.
Speak to your doctor if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome:
More common: dry mouth.
Less common or rare: abdominal or stomach cramps or pain; blurred or double vision; confusion; constipation; difficulty in urination; dizziness or light-headedness; drowsiness; excitement, indigestion, irritability, nausea, nervousness or restlessness; headache; muscle weakness; unusually large pupils of the eyes.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some patients.
If you notice any side effects that are not listed here tell your doctor or pharmacist.
After taking Norgesic
Storage
Keep this medicine in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C. Do not store it or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it on a window sill or in the car. Keep all medicines where children cannot reach them. A locked cupboard at least 1.5 metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking this medicine, or if it has passed its 'Use By' date ask your pharmacist what to do with any tablets that are left over.
Product Description
What it looks like
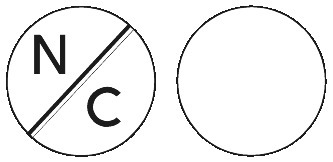
Norgesic are white tablets with N/C marked on one side and no marking on the other side, in bottles containing 100 tablets, 24 tablets and 8 tablets and blisters containing 24 tablets.
Ingredients
Each Norgesic tablet contains 35mg orphenadrine citrate and 450mg paracetamol.
It also contains:
- Magnesium Stearate
- Colloidal Anhydrous Silica
- Microcrystalline Cellulose
- Starch 1500
This medicine does not contain gluten.
Sponsor
Norgesic is supplied in Australia by:
iNova Pharmaceuticals (Australia) Pty Limited
ABN 13 617 871 539
L10, 12 Help Street
Chatswood NSW 2067
Tel: 1800 630 056
Australian Registration Number:
AUST R 10574 (bottles)
AUST R 156623 (blister)*
This leaflet was prepared in November 2017
* Not currently marketed in Australia
Published by MIMS August 2025

 C18H23NO.C6H8O7. M.W. 461.51.
C18H23NO.C6H8O7. M.W. 461.51.
