What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about PANADOL. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your pharmacist or doctor.
All medicines have risks and benefits.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What PANADOL is used for
The active ingredient in these medicines is paracetamol.
Paracetamol is used for the fast effective temporary relief of pain and discomfort associated with various pain states including:
- Headache
- Muscular aches
- Period pain
- Arthritis/Osteoarthritis
- Toothache
- Migraine headache
- Colds and flu symptoms
- Tension headache
- Sinus pain/headache
- Backache
Paracetamol also reduces fever.
Paracetamol works to stop the pain messages from getting through to the brain. It also acts in the brain to reduce fever.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you have any questions about this medicine. Your pharmacist or doctor may have given it for another reason.
Before you use PANADOL
Do not take more than the recommended dose as it may cause serious harm to your liver.
When you must not use it
Do not use PANADOL if you have an allergy to:
- Any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Do not use this medicine if you are taking any other prescription or non-prescription medicines containing paracetamol to treat pain, fever, symptoms of cold and flu, or to aid sleep.
Always read and follow the label.
Do not take this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
If you are not sure whether you should start using this medicine, talk to your pharmacist or doctor.
Before you start to use it
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions:
- Liver or kidney problems
- Are underweight or malnourished
- Regularly drink alcohol
You may need to avoid using this product altogether or limit the amount of paracetamol that you take. - You have a severe illness, severe infection including blood infection, are severely malnourished or are a chronic heavy alcohol user as this may increase the risk of metabolic acidosis (a blood and fluid abnormality). Signs of metabolic acidosis include:
- deep, rapid, difficult breathing
- feeling sick (nausea), being sick (vomiting)
- loss of appetite
- drowsiness
Contact a doctor immediately if you think you may be affected.
Please see your doctor if your symptoms do not improve.
Keep out of sight and reach of children.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor about using paracetamol if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. Paracetamol may be used during pregnancy and if you are breastfeeding but you should always consult your doctor first.
Consider taking the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time.
If you have not told your pharmacist or doctor about any of the above, tell them before you use PANADOL.
Using other medicines
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you are using any other medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and paracetamol may interfere with each other. These include:
- Warfarin or similar medicines used to thin the blood
- Metoclopramide, a medicine used to control nausea and vomiting
- Medicines used to treat epilepsy or fits
- Chloramphenicol, an antibiotic used to treat ear and eye infections
- Alcohol
- Probenecid, a medicine used to treat gout or sometimes given with an antibiotic
- Cholestyramine, a medicine used to treat high cholesterol levels in the blood
- Flucloxacillin (an antibiotic), due to a serious risk of blood and fluid abnormality (metabolic acidosis)
Your pharmacist and doctor will have more information on these and other medicines to be careful with or avoid while using this medicine.
How to use PANADOL
Follow all directions given to you by your pharmacist or doctor carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the box/bottle, ask your pharmacist or doctor for help.
Do not exceed the stated dose and do not take more frequently than every four hours.
Use the smallest dose that you need to treat your symptoms and use the medicine for the shortest period of time necessary.
How much to use
PANADOL Tablets
Adults and children aged 12 years and over: Take 1 to 2 tablets every four to six hours as needed. Do not take more than 8 tablets in 24 hours.
Children 7 to 12 years: Take ½ to 1 tablet every four to six hours as needed. Do not take more than 4 tablets in 24 hours.
Not recommended in children under 7 years.
PANADOL Mini Caps
Adults and children aged 12 years and over: Take 1 to 2 caplets every four to six hours as needed. Do not take more than 8 caplets in 24 hours.
Children 7 to 12 years: Take 1 caplet every four to six hours as needed. Do not take more than 4 caplets in 24 hours.
Do not use in children under 7 years.
How to use it
PANADOL Tablets and Mini Caps
Swallow with water or other fluid.
How long to use it
PANADOL Tablets and Mini Caps
Adults:
Only take paracetamol for a few days at a time unless your doctor tells you to take it for longer.
Children 7 to 17 years:
Only give paracetamol to children for up to 48 hours unless a doctor has told you to give it for longer.
If you use too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone 13 11 26 for Australia, 0800 764 766 for New Zealand) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much PANADOL. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning because of the risk of delayed, serious liver damage/failure if left untreated. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are using PANADOL
Things you must do
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor if your symptoms do not improve. Your pharmacist or doctor will assess your condition and decide if you should continue to take the medicine.
Things you must not do
Children:
Do not give paracetamol for more than 48 hours unless a doctor has told you to.
Adults:
Do not use for more than a few days at a time unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not take more than the recommended dose unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not use PANADOL to treat any other complaints unless your pharmacist or doctor tells you to.
Things to be careful of
Only drink small quantities of alcohol (beer, wine or spirits) while using paracetamol. Drinking large quantities of alcohol while taking paracetamol may increase the risk of liver side effects.
Side effects
Tell your pharmacist or doctor as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are using PANADOL.
This medicine helps most people with various types of pain but it may have unwanted side effects. All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor to answer any questions you may have.
If any of the following happen, stop use and tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat or other parts of the body
- Allergic skin reaction such as rash, peeling, itching or hives
- Mouth ulcers
- Unexplained bruising or bleeding
- Symptoms of metabolic acidosis which may include: serious breathing difficulties with deep rapid breathing, drowsiness, feeling sick (nausea), being sick (vomiting) and loss of appetite
The above list includes very serious side effects of your medicine. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
After using PANADOL
Storage
Keep your medicine in the original pack until it is time to take it.
Keep your medicine in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C for PANADOL Tablets and below 25°C for PANADOL Mini Caps.
Do not store PANADOL or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it on a window sill or in the car. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
Ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over, or if the expiry date has passed.
Product description
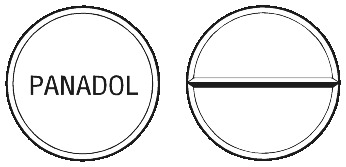
What it looks like
PANADOL Tablets are a white, film-coated round tablet. They are marked "PANADOL" on one side and have a break bar on the other side.
PANADOL Mini Caps are a capsule-shaped tablet with a gelatin coating. One half is green and the other half is white.
Ingredients
PANADOL Tablets contain 500 mg of paracetamol as the active ingredient.
They also contain:
- Starch-pregelatinised maize
- Starch-maize
- Talc-purified
- Stearic acid
- Hypromellose
- Povidone
- Glycerol triacetate
- Potassium sorbate
- Carnauba wax
Contains potassium sorbate as a preservative.
PANADOL Mini Caps contains paracetamol 500 mg as the active ingredient.
They also contain:
- Gelatin capsules hard
- Starch-pregelatinised maize
- Croscarmellose sodium
- Povidone
- Stearic acid
- Hypromellose
- Titanium dioxide
- Quinoline yellow
- Brilliant blue FCF
- Allura red AC
Manufacturer/ Supplier
Haleon Australia
Level 48, 8 Parramatta Square,
10 Darcy Street, Parramatta NSW
2150 and Auckland, New Zealand
AUST R 13591 (PANADOL Tablets)
AUST R 81007 (PANADOL Mini Caps)
Date of Preparation July 2025
Trademarks are owned by or licensed to Haleon.
Published by MIMS September 2025