1 Name of Medicine
Paracetamol.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Active ingredient.
Paracetamol 665 mg/tablet.
Excipients.
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1 List of Excipients.3 Pharmaceutical Form
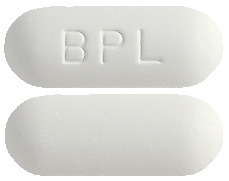
Parapane Osteo is a bi-layer white colored capsule shaped film coated tablet, engraved BPL on one side and plain on the other.
4.1 Therapeutic Indications
Parapane Osteo provides effective relief from persistent pain for up to 8 hours. Effective for the relief of persistent pain associated with osteoarthritis and muscular aches and pains such as backache. Parapane Osteo also provides effective temporary relief of pain and discomfort associated with: headache, tension headache, cold and flu, period pain, toothache and pain after dental procedures. Reduces fever.
4.2 Dose and Method of Administration
Adults and children aged 12 years and over: 2 tablets swallowed whole three times a day every 6 to 8 hours. Do not chew or suck, as it impairs the sustained release properties. Maximum of 6 tablets in 24 hours.
Do not use for more than a few days at a time in adults except on medical advice.
Children under 12 years: Not recommended for children under the age of 12 years.
Should not be used for more than 48 hours for children aged 12-17 years except on medical advice.
Take with water or other fluid.
Can be taken with or without food.
Doses should be equally spaced throughout the day.
The tablets must not be crushed.
Do not exceed the stated dose.
The lowest dose necessary to achieve efficacy should be used for the shortest duration of treatment.
Should not be used with other paracetamol-containing products.
Minimum dosing interval: 6 hours.
Maximum daily dose for children 12 years of age to adults: 4000 mg.
4.3 Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with a previous history of hypersensitivity to paracetamol or to any of the excipients.
4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
Identified precautions.
Contains paracetamol. Do not use with any other paracetamol-containing products. The concomitant use with other products containing paracetamol may lead to an overdose.
Paracetamol overdose may cause liver failure which may require liver transplant or lead to death.
If symptoms persist, medical advice must be sought.
Keep out of sight and reach of children.
Use in hepatic impairment.
Paracetamol should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver function: underlying liver disease increases the risk of paracetamol-related liver damage.
Patients who have been diagnosed with liver impairment must seek medical advice before taking this medication. The restrictions related to the use of paracetamol products in patients with hepatic impairment are primarily a consequence of the paracetamol content of the drug.
Cases of hepatic dysfunction/failure have been reported in patients with depleted glutathione levels, such as those who are severely malnourished, anorexic, have a low body mass index, are chronic heavy users of alcohol or have sepsis.
In patients with glutathione depleted states the use of paracetamol may increase the risk of metabolic acidosis.
Use in renal impairment.
Paracetamol should be used with caution in patients with impaired kidney function: administration of paracetamol to patients with moderate to severe renal impairment may result in accumulation of paracetamol conjugates.
Patients who have been diagnosed with kidney impairment must seek medical advice before taking this medication.
Use in the elderly.
No data available.
Paediatric use.
Not recommended for children under 12 years of age.
Effects on laboratory tests.
No data available.4.5 Interactions with Other Medicines and Other Forms of Interactions
The following interactions with paracetamol have been noted:
The anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other coumarins may be enhanced by prolonged regular daily use of paracetamol with increased risk of bleeding; occasional doses have no significant effect. Anticoagulant dosage may require reduction if paracetamol and anticoagulants are taken for a prolonged period of time.
Paracetamol absorption is increased by substances that increase gastric emptying, e.g. metoclopramide.
Paracetamol absorption is decreased by substances that decrease gastric emptying, e.g. propantheline, antidepressants with anticholinergic properties, and narcotic analgesics.
Paracetamol may increase chloramphenicol concentrations.
The risk of paracetamol toxicity may be increased in patients receiving other potentially hepatotoxic drugs or drugs that induce liver microsomal enzymes such as alcohol and anticonvulsant agents.
Paracetamol excretion may be affected and plasma concentrations altered when given with probenecid.
Colestyramine reduces the absorption of paracetamol if given within 1 hour of paracetamol.
4.6 Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
Effects on fertility.
No data available.
(Category A)
Paracetamol has been taken by a large number of pregnant women and women of childbearing age without any proven increase in the frequency of malformations or other direct or indirect harmful effects on the foetus having been observed.
As with the use of any medicine during pregnancy, pregnant women should seek medical advice before taking paracetamol. The lowest effective dose and shortest duration of treatment should be considered.
Paracetamol is excreted in breast milk. Human studies with paracetamol have not identified any risk to lactation or the breast-fed offspring. These results are based on immediate release preparations of paracetamol. There is no data available on the excretion of sustained-release paracetamol preparations in breast milk. However, it is not expected that Parapane Osteo would provide any increase in the excretion of paracetamol in breast milk as this product is designed to maintain rather than increase plasma paracetamol concentrations compared to immediate release preparations. Maternal ingestion of paracetamol in usual analgesic doses does not appear to present a risk to the breastfed infant.4.7 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
The effects of this medicine on a person's ability to drive and use machines were not assessed as part of its registration.
4.8 Adverse Effects (Undesirable Effects)
Reporting suspected adverse effects.
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after registration of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit-risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems.
Adverse events from historical clinical trial data are both infrequent and from small patient exposure. Accordingly, events reported from extensive post-marketing experience at therapeutic/labelled doses and considered attributable are tabulated in Table 1 by System Organ Class and frequency.
The following convention has been utilised for the classification of undesirable effects: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100, < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000, < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000, < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000), not known (cannot be estimated from available data).
Adverse event frequencies have been estimated from spontaneous reports received through post-marketing data.

4.9 Overdose
If an overdose is taken or suspected, the patient should go to the nearest hospital straight away. This should be done even if they feel well because of the risk of delayed, serious liver damage (see Section 4.8 Adverse Effects (Undesirable Effects)).
For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (Australia).
Because Parapane Osteo is a sustained-release formulation of paracetamol, absorption will be prolonged in overdose. It is recommended that for the management of overdose, where Parapane Osteo is suspected, that an additional plasma paracetamol level be obtained 4-6 hours after the initial measurement. If either level is above or close to the treatment line on the paracetamol overdose nomogram, administration of antidote would be indicated.
Treatment.
Paracetamol overdose may cause liver failure which may require liver transplant or lead to death. Acute pancreatitis has been observed, usually with hepatic dysfunction and liver toxicity.
Immediate medical management is required in the event of an overdose, even if the symptoms of overdose are not present.
Administration of N-acetylcysteine may be required.
In cases of overdosage, methods of reducing absorption of ingested drug are important. Activated charcoal may reduce absorption of the medicine if given within one hour after oral ingestion. In patients who are not fully conscious or have impaired gag reflex, consideration should be given to administering activated charcoal via a nasogastric tube, once the airway is protected.5 Pharmacological Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic Properties
Mechanism of action.
Paracetamol is a para-aminophenol derivative that exhibits analgesic and anti-pyretic activity. Its mechanism of action is believed to include inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, primarily within the central nervous system. It does not possess anti-inflammatory activity. It provides relief from mild to moderate pain and fever.
The combination of immediate release and sustained release paracetamol provides pain relief, which may last up to 8 hours.
Clinical trials.
Chronic pain.
In patients with pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, sustained release paracetamol (2 tablets taken three times daily) and standard immediate release paracetamol (2 tablets taken 4 times daily) were clinically equivalent at a total daily dose of 4 g based on patient global assessment after treatment for 7 days.
Sustained release paracetamol and standard immediate release paracetamol were not significantly different for a range of secondary efficacy parameters including pain during the day, pain on walking, pain relief, number of times woken during the night due to pain and duration of morning stiffness.
Since sustained release paracetamol (three times daily) was clinically equivalent to standard immediate release paracetamol (four times daily), it was concluded that sustained release paracetamol provides pain relief for up to 8 hours after dosing.
Acute pain.
In patients with post-surgical dental pain, a single dose of sustained release paracetamol (2 tablets) was therapeutically equivalent to standard immediate release paracetamol (2 tablets) based on patient global assessment 4 hours after treatment. Onset of action was apparent 30 minutes after administration.
There was no significant difference between sustained release paracetamol and standard immediate release paracetamol in either development of analgesia or peak analgesic effect. Trends in favour of sustained release paracetamol were observed at the later time points. Furthermore, sustained release paracetamol was significantly more effective than standard immediate release paracetamol for the summed pain intensity difference at 6 hours (p = 0.0344) and 8 hours (p = 0.0500), as measured on a visual analogue scale.
Summary.
From these results, it was concluded that sustained release paracetamol has a similar time to onset of action compared to standard immediate release paracetamol and provides more prolonged analgesia than standard immediate release paracetamol. For the patient, this translates to longer lasting pain relief and the improved convenience of fewer doses. This is as expected for a formulation containing sustained release paracetamol and consistent with results from the pharmacokinetic studies.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties
Absorption.
Paracetamol is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Food intake delays paracetamol absorption.
Parapane Osteo is a unique bi-layer tablet incorporating an immediate release and a sustained release dose of paracetamol.
The sustained release layer contains HPMC polymer, which rapidly hydrates to form a gel layer at the matrix periphery. The drug is then released from the matrix by a combination of diffusion and erosion of the gel layer.
Parapane Osteo releases drug at a rate which ensures that therapeutically active plasma paracetamol concentrations are rapidly attained and maintained until up to 8 hours after administration.
Food had little effect on the extent of paracetamol absorption from Parapane Osteo demonstrating that Parapane Osteo is suitable to be taken with or without meals. Paracetamol was rapidly absorbed after administration of Parapane Osteo and was generally measurable in plasma within 15 minutes in fasted subjects. Mean plasma paracetamol concentrations above the minimum level required for analgesia (> 4 microgram/mL) were maintained until up to 6 to 7 hours after administration in fasted subjects and 7 to 8 hours in fed subjects.
Distribution.
Paracetamol is distributed into most body tissues. Binding to the plasma proteins is minimal at therapeutic concentrations but increases with increasing doses.
Metabolism.
Paracetamol is metabolised extensively in the liver and excreted in the urine mainly as inactive glucuronide and sulphate conjugates.
The metabolites of paracetamol include a minor hydroxylated intermediate which has hepatotoxic activity. This intermediate metabolite is detoxified by conjugation with glutathione. However, it can accumulate following paracetamol overdosage (more than 150 mg/kg or 10 g total paracetamol ingested) and, if left untreated, can cause irreversible liver damage.
Paracetamol is metabolised differently by premature infants, newborns, infants and young children compared to adults, the sulfate conjugate being predominant.
Excretion.
Paracetamol is excreted in the urine mainly as the glucuronide and sulfate conjugates. Less than 5% is excreted unchanged. Approximately 85% of a dose of paracetamol is excreted in urine as free and conjugated paracetamol within 24 hours of ingestion. Administration of paracetamol to patients with moderate to severe renal impairment may result in accumulation of paracetamol conjugates. The elimination half-life varies from one to three hours.
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity.
No data available.
Carcinogenicity.
No data available.6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.1 List of Excipients
The tablets contain hyetellose, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, pregelatinized starch, magnesium stearate, maize starch, sodium starch glycolate, stearic acid, Opadry KB low viscosity film coating system 310A180023 White and carnauba wax.
The tablets are sugar, lactose and gluten free.
6.2 Incompatibilities
Incompatibilities were either not assessed or not identified as part of the registration of this medicine.
6.3 Shelf Life
In Australia, information on the shelf-life can be found on the public summary of the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG). The expiry date can be found on the packaging.
6.4 Special Precautions for Storage
Store below 30°C.
6.5 Nature and Contents of Container
Alu-PVDC blister packs of 24, 48 and 96 tablets.
HDPE bottles of 96 tablets with child resistant closure.
HDPE bottles for dispensing by pharmacists only of 192 and 1000 tablets.
6.6 Special Precautions for Disposal
In Australia, any unused medicine or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Active ingredients.
Paracetamol.
Chemical structure.
 Chemical name: N-acetyl-p-aminophenol.
Chemical name: N-acetyl-p-aminophenol.
Molecular formula: C8H9NO2.
Molecular weight: 151.17.
CAS number.
103-90-2.7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
S3 - Pharmacist only medicine.
Summary Table of Changes



 Chemical name: N-acetyl-p-aminophenol.
Chemical name: N-acetyl-p-aminophenol.