Notes
Distributed by Generic Health Pty Ltd
1 Name of Medicine
Promethazine hydrochloride.
2 Qualitative and Quantitative Composition
Pharmacy Action Allerelief 10.
10 mg tablet contains promethazine hydrochloride 10 mg as an active ingredient.
Pharmacy Action Allerelief 25.
25 mg tablet contains promethazine hydrochloride 25 mg as an active ingredient.
This formulation contains lactose monohydrate (sugars) as an excipient with known effect.
For the full list of excipients, see Section 6.1. List of Excipients.3 Pharmaceutical Form
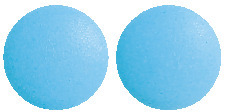
Pharmacy Action Allerelief 10 mg and 25 mg are blue coloured, round, biconvex, film-coated tablets which are plain on both sides.
4.1 Therapeutic Indications
Allergies.
Treatment of allergic conditions including some allergic reactions to drugs, urticaria and allergic contact dermatitis, and allergic reactions to insect bites and stings.
Upper respiratory tract.
Relief of excessive secretion in the upper respiratory tract as a result of hay fever and allergic rhinitis.
Nausea and vomiting.
Antiemetic for vomiting from various causes, including postoperative vomiting, irradiation sickness, drug induced nausea and motion sickness.
Sedation.
For short-term use under the advice of a doctor or pharmacist. Do not use for more than 7 to 10 consecutive days.
Other.
Promethazine has sedative effects and can be used in the symptomatic management of measles and chicken pox. Promethazine can be used as a preanesthetic medication for the prevention and control of post-operative vomiting.4.2 Dose and Method of Administration
This product should not be given to children under 6 years of age. This product should be given to children aged between 6 and 11 years only on the advice of a doctor, pharmacist or nurse practitioner (see Section 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use). Dosage varies according to the condition being treated and the individual's response.
Allergic disorders.
Children 6-12 years.
10 to 25 mg as a single dose at night, or 10 mg two to three times daily.
Adults and children over 12 years.
25 to 75 mg as a single dose at night, or 10 to 20 mg two to three times daily.
Sedation.
Children 6-12 years.
10 to 25 mg as a single dose at night.
Adults and children over 12 years.
25 to 75 mg as a single dose at night.
Travel sickness prevention.
Children 6-12 years.
10 mg.
Adults and children over 12 years.
10 mg to 25 mg.
To be taken the night before travel and repeated after 6 to 8 hours on the following day if required.
Travel sickness treatment.
Children 6-12 years.
10 mg.
Adults and children over 12 years.
10 mg to 25 mg.
Nausea and vomiting.
Children 6-12 years.
10 mg, 2 times a day to a maximum daily dose of 20 mg.
Adults and children over 12 years.
25 mg, 3 to 4 times a day to a maximum daily dose of 100 mg.4.3 Contraindications
Promethazine is contraindicated for use in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug substance, substances of similar chemical structure or hypersensitivity to the other ingredients.
Promethazine is contraindicated for use in:
newborns or premature infants;
children under 6 years of age (see Section 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use);
women who are lactating/breastfeeding;
patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) (see Section 4.5 Interactions with Other Medicines and Other Forms of Interactions);
jaundice induced by other phenothiazine derivatives;
patients who have received high doses of other CNS depressants and/or are comatose.
See Section 4.5 Interactions with Other Medicines and Other Forms of Interactions.
4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
Caution is advised in patients with:
cardiovascular disease;
acute or chronic respiratory impairment, promethazine may thicken or dry lung secretions and impair expectoration;
epilepsy, as epileptic patients may experience increased severity of convulsions;
hypertensive crisis or a history of hypertensive crisis;
narrow-angle glaucoma;
stenosing peptic ulcer;
symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy;
bladder neck obstruction;
pyloroduodenal obstruction;
eczema or a tendency to rheumatism, as solar dermatitis has been reported following oral doses of promethazine in these patients;
a history of drug abuse, as cases of drug abuse have been reported with promethazine.
Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, urticaria and angioedema have been reported with promethazine use. In case of allergic reaction, treatment with promethazine must be discontinued and appropriate symptomatic treatment initiated - see Section 4.5.
Promethazine should be avoided in patients with Parkinson's disease, hypothyroidism, cardiac failure, pheochromocytoma, myasthenia gravis, or prostate hypertrophy, or in patients with a history of agranulocytosis.
Caution must be exercised when using H1-antihistamines such as promethazine due to the risk of sedation.
Combined use with other sedative medicinal products is not recommended (see Section 4.5).
Promethazine may delay the early diagnosis of intestinal obstruction or increased intracranial pressure through the suppression of vomiting.
Promethazine may mask the warning signs of ototoxicity caused by ototoxic drugs e.g. salicylates.
Promethazine may increase the effects of alcohol. Alcohol should be avoided during treatment.
QT prolongation.
QT interval prolongation has been reported with phenothiazines.
Phenothiazine derivatives may potentiate QT interval prolongation which increases the risk of onset of serious ventricular arrhythmias of the torsade de pointes type, which is potentially fatal (sudden death).
QT prolongation is exacerbated, in particular, in the presence of bradycardia, hypokalaemia, and acquired (i.e. drug induced) QT prolongation. If the clinical situation permits, medical and laboratory evaluations should be performed to rule out possible risk factors before initiating treatment with a phenothiazine derivative and as deemed necessary during treatment (see Section 4.8 Adverse Effects (Undesirable Effects)).
See Section 4.5 Interactions with Other Medicines and Other Forms of Interactions for additional information.
Other precautions.
Prolonged administration of any phenothiazine may result in tardive dyskinesia, particularly in the elderly and children.
Alcohol and alcohol-containing medicines should be avoided while on this medicine (see Section 4.5).
Phenothiazines may be additive with, or may potentiate the action of, other CNS depressants such as opiates or other analgesics, barbiturates or other sedatives, general anesthetics, or alcohol.
As agranulocytosis has been reported, regular monitoring of the complete blood count is recommended. The occurrence of unexplained infections or fever may be evidence of blood dyscrasia (see Section 4.5), and requires immediate haematological investigation.
All patients should be advised that, if they experience fever, sore throat or any other infection, they should inform their physician immediately and undergo a complete blood count. Treatment should be discontinued if any marked changes (hyperleucocytosis, granulocytopenia) are observed in the blood count.
There have been case reports of drug abuse with promethazine. The risk of abuse is greater in patients with a history of drug abuse.
Hypertensive crisis.
Promethazine should be used with caution, if at all, in these patients.
Epilepsy.
Epileptic patients may experience increased severity of convulsions.
Skin reactions.
Solar dermatitis has been reported following oral doses of Pharmacy Action Allerelief in patients with eczema or a tendency to rheumatism.
Due to the risk of photosensitivity, exposure to the sun or ultraviolet light should be avoided during or shortly after treatment.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
As with neuroleptics, neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) characterised by hyperthermia, extrapyramidal disorders, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, autonomic nervous instability and elevated CPK, may occur. As this syndrome is potentially fatal, promethazine must be discontinued immediately, and intensive clinical monitoring and symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
Use in hepatic impairment.
Caution is advised in patients with hepatic insufficiency. It should be avoided in patients with liver dysfunction.
Use in renal impairment.
Caution is advised in patients with renal failure or insufficiency. It should be avoided in patients with renal dysfunction.
Use in the elderly.
The elderly may experience paradoxical excitation with promethazine. The elderly are more likely to have CNS depressive side effects, including confusion and are more susceptible to the antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines, including hypotension (see Section 4.3 Contraindications).
Paediatric use.
Do not use promethazine hydrochloride in children under 6 years of age due to the potential for fatal respiratory depression (see Section 4.3 Contraindications).
The use of promethazine should be avoided in children and adolescents with signs or symptoms of Reye's syndrome.
Caution should be exercised when administering promethazine to children as there is potential for central and obstructive apnoea and reduced arousal. Excessive dosages of antihistamines in children may cause hallucinations, convulsions and sudden death. Children may experience paradoxical excitation with promethazine.
Concomitant administration of other drugs with respiratory depressant effects should be avoided.
The use of promethazine should be avoided in children and adolescents with signs and symptoms suggestive of Reye's syndrome.
Effects on laboratory tests.
Combination with alcohol enhances the sedative effects of H1 antihistamines. Promethazine may interfere with immunological urine pregnancy tests to produce false-positive or false-negative results.
Promethazine should be discontinued at least 72 hours before the start of skin tests, as it may inhibit the cutaneous histamine response thus producing false-negative results.4.5 Interactions with Other Medicines and Other Forms of Interactions
Promethazine will enhance the action of any anticholinergic agent, tricyclic antidepressant, sedative or hypnotic. Promethazine may cause drowsiness and will enhance the sedative effects of CNS depressants (including alcohol, barbiturates, hypnotics, opioid analgesics, anxiolytic sedatives and neuroleptics), and have additive antimuscarinic actions with other antimuscarinic drugs (atropine, tricyclic antidepressants). Interactions between promethazine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) may prolong and intensify the anticholinergic and CNS depressive effects.
Alcohol should be avoided during treatment.
Special caution is required when promethazine is used concurrently with drugs known to cause QT prolongation (such as antiarrhythmics, antimicrobials, antidepressants, antipsychotics) to avoid exacerbation of risk of QT prolongation.
Cytochrome P450 2D6 metabolism.
Some phenothiazines are moderate inhibitors of CYP2D6. There is a possible pharmacokinetic interaction between inhibitors of CYP2D6, such as phenothiazines, and CYP2D6 substrates. Co administration of promethazine with amitriptyline/ amitriptylinoxide, a CYP2D6 substrate, may lead to an increase in the plasma levels of amitriptyline/ amitriptylinoxide. Monitor patients for dose-dependent adverse reactions associated with amitriptyline/amitriptylinoxide.
Promethazine should be avoided in patients taking monamine oxidase inhibitors within the previous 14 days, and monamine oxidase inhibitors should be avoided while using promethazine.
Seizure threshold-lowering drugs.
Concomitant use of seizure-inducing drugs or seizure threshold lowering drugs should be carefully considered due to the severity of the risk for the patient (see Section 4.4).
Gastro-intestinal agents that are not absorbed (magnesium, aluminium and calcium salts, oxides and hydroxides).
Reduced gastro-intestinal absorption of phenothiazines may occur. Such gastrointestinal agents should not be taken at the same time as phenothiazines (at least 2 hours apart, if possible).
Drugs with anticholinergic properties.
Concomitant use of promethazine with drugs with anticholinergic properties enhances the anticholinergic effect.4.6 Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
Effects on fertility.
No data available.
(Category C)
The use of promethazine is not recommended during pregnancy and in women of childbearing potential not using contraception. Promethazine, owing to its pharmacological effects, has caused or may be suspected of causing, harmful effects on the human foetus or neonate without causing malformations.
These effects may be reversible. When promethazine has been given in high doses during late pregnancy, promethazine has caused prolonged neurological disturbances in the infant. Promethazine should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefits to the patient are weighed against the possible risk to the foetus.
There are no available animal studies regarding reproductive toxicity.
Promethazine is excreted in breast milk. There are risks of neonatal irritability and excitement. Therefore, it should not be used for breastfeeding women.4.7 Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
This medication may cause drowsiness and may increase the effects of alcohol. Patients receiving promethazine hydrochloride for the first time should not be in control of vehicles or machinery for the first few days until it is established that they are not hypersensitive to the central nervous effects of the medicine and do not suffer from disorientation, confusion or dizziness. Those affected should not drive a motor vehicle or operate machinery.
4.8 Adverse Effects (Undesirable Effects)
CNS effects.
CNS depressive effects of promethazine include sedation and impaired performance (impaired driving performance, poor work performance, incoordination, reduced motor skills, and impaired information processing). Performance may be impaired in the absence of sedation and may persist the morning after a night-time dose.
The CNS stimulatory effects of promethazine may include anxiety, hallucinations, appetite stimulation, muscle dyskinesias and activation of epileptogenic foci.
High doses of promethazine may cause nervousness, tremor, insomnia, agitation, and irritability.
Anticholinergic effects.
Side effects of promethazine associated with cholinergic blockage include dryness of the eyes, mouth and nose, blurred vision, urinary hesitancy and retention, constipation and tachycardia.
More common reactions.
Gastrointestinal.
Dry mouth, epigastric distress, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhoea.
Nervous system.
Sedation or somnolence, restlessness, dizziness, lassitude, incoordination, fatigue.
Ocular.
Blurred vision.
Less common reactions.
Cardiovascular.
Tachycardia, bradycardia, faintness.
Dermatological.
Contact dermatitis (topical), photosensitization, urticaria, angioneurotic oedema, pruritus.
Haematological.
Leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, thrombocytopenic purpura
Hepatic.
Jaundice.
Musculoskeletal.
Extrapyramidal symptoms.
Nervous system.
Tinnitus, euphoria, nervousness, insomnia, convulsive seizures, oculogyric crises, excitation, catatonic-like states, hysteria, extrapyramidal symptoms, tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS).
Respiratory.
Marked irregular respiration.
Severe or life-threatening reactions.
Agranulocytosis, anaphylaxis.
Reactions with frequency unknown.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders.
Rash, photosensitivity.
Hepatobiliary disorders.
Jaundice cholestatic.
Renal and urinary disorders.
Urinary retention.
Nervous system disorders.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome, somnolence, dizziness, headaches, tic-like movements of the head and face, extrapyramidal symptoms including muscle spasm. Dystonia, including oculogyric crisis, usually transitory are commoner in children and young adults, and usually occur within the first 4 days of treatment or after dosage increases. Anticholinergic effects such as ileus paralytic, risk of urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation, accommodation disorder. The elderly are particularly susceptible to the anticholinergic effects and confusion due to promethazine.
Immune system disorders.
Allergic reactions, including anaphylactic reaction, urticaria, rash, pruritus, angioedema and anaphylactic reaction have been reported.
Metabolism and nutrition disorders.
Anorexia, decreased appetite.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders.
Blood dyscrasias including haemolytic anaemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, eosinophilia, thrombocytopenia (including thrombocytopenic purpura).
Psychiatric disorders.
Agitation, confusional state, anxiety. Infants, newborns and premature are susceptible to the anticholinergic effects of promethazine, while other children may display paradoxical hyperexcitability, restlessness, nightmares, disorientation.
Cardiac disorders.
Palpitations, arrhythmias, QT prolongation, torsade de pointes.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders.
Respiratory depression, nasal congestion.
Vascular disorders.
Hypotension.
General disorders and administration site conditions.
Tiredness.
Reporting suspected adverse effects.
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after registration of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit-risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems.4.9 Overdose
The chief sign of acute poisoning from ingestion of an overdose of promethazine is unconsciousness, which is commonly delayed. In addition, convulsions, hallucinations, delirium, acute anxiety, psychotic reactions, extreme hyperesthesia and hyperalgesia with extensor plantar responses may occur.
Anticholinergic action may cause tachycardia, flushed skin, dry mouth and sometimes mydriasis and urinary retention.
Symptoms of severe overdosage are variable. The chief sign of acute poisoning from ingestion of an overdose of promethazine is unconsciousness, which is commonly delayed. In addition, convulsions, hallucinations, delirium, acute anxiety, psychotic reactions, extreme hyperaesthesia and hyperalgesia with extensor plantar responses may occur. Anticholinergic action may cause tachycardia, flushed skin, dry mouth and sometimes mydriasis and urinary retention.
High doses can cause ventricular arrhythmias including QT prolongation and torsade de pointes (see Section 4.8 Adverse Effects (Undesirable Effects)).
In adults, CNS depression is more common, with drowsiness, coma, convulsions, progressing to respiratory failure or cardiovascular collapse.
In infants and children, CNS stimulation predominates over CNS depression causing ataxia, excitement, tremors, psychoses, hallucinations, convulsions and possibly hyperpyrexia, which may be followed by deepening coma and cardiorespiratory collapse.
Symptomatic supportive therapy is indicated and maintenance of adequate ventilation should be instituted if necessary.
Treatment.
Similar to that of other phenothiazines. In the event of overdose of promethazine, take all appropriate measures immediately. For information on the management of overdose, contact the Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26 (Australia).
Symptomatic supportive therapy is indicated and maintenance of adequate ventilation should be instituted if necessary.5 Pharmacological Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic Properties
Mechanism of action.
Promethazine, a phenothiazine derivative, is a long acting antihistamine with mild atropine-like anticholinergic effects and some anti-serotonin effects, and because of its marked effect on the central nervous system (CNS), it acts as an antiemetic, hypnotic, tranquilliser, and a potentiator of anaesthetics, hypnotics, sedatives and analgesic.
Clinical trials.
No data available.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic Properties
Absorption.
Promethazine hydrochloride is well absorbed from the GI tract and from parenteral sites after oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are reached 2 to 3 hours after administration by this route, although there is low systemic bioavailability after oral administration, due to high first-pass metabolism in the liver.
Distribution.
Promethazine hydrochloride is widely distributed within body tissues. It is highly bound to plasma proteins (76-93%). Promethazine crosses the blood-brain barrier, and the placenta and is excreted in breast milk.
Metabolism.
Promethazine hydrochloride is metabolized in the liver. Promethazine undergoes extensive metabolism, predominantly to promethazine sulfoxide, and also to N-desmethylpromethazine.
Excretion.
Promethazine hydrochloride is slowly excreted via urine and bile, mainly as metabolites. Elimination half-lives of 5 to 14 hours have been reported. The antihistamine action has been reported to be between 4 and 12 hours.
5.3 Preclinical Safety Data
Genotoxicity.
No data available.
Carcinogenicity.
No data available.6 Pharmaceutical Particulars
6.1 List of Excipients
Following are the list of excipients present in the formulation of 10 mg and 25 mg promethazine hydrochloride tablets: povidone; maize starch; lactose monohydrate; magnesium stearate; Opadry complete film coating system 03B505083 blue (PI 114196).
6.2 Incompatibilities
Incompatibilities were either not assessed or not identified as part of the registration of this medicine.
6.3 Shelf Life
In Australia, information on the shelf life can be found on the public summary of the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG). The expiry date can be found on the packaging.
6.4 Special Precautions for Storage
Store below 25°C. Protect from light.
6.5 Nature and Contents of Container
Aluminium/opaque PVC film blisters in packs of 50 tablets.
Australian registration numbers.
Pharmacy Action Allerelief 10.
10 mg: AUST R 328721.
Pharmacy Action Allerelief 25.
25 mg: AUST R 328720.
6.6 Special Precautions for Disposal
In Australia, any unused medicine or waste material should be disposed of by taking to your local pharmacy.
6.7 Physicochemical Properties
Chemical structure.
 Structural formula: C17H20N2S.HCl.
Structural formula: C17H20N2S.HCl.
Molecular weight: 320.9.
CAS number.
58-33-3.7 Medicine Schedule (Poisons Standard)
Schedule 3 - Pharmacist Only Medicine.
Summary Table of Changes



 Structural formula: C17H20N2S.HCl.
Structural formula: C17H20N2S.HCl.