What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE tablets.
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your pharmacist or doctor.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your pharmacist or doctor has weighed the risks of you taking PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE is used for
This product is used for temporary relief of symptoms of:
- Sinus headache;
- Pain and nasal congestion (including fever) and hayfever.
Paracetamol works to stop the pain messages from getting through to the brain. It also acts in the brain to reduce fever.
Pseudoephedrine belongs to a group of medicines called sympathomimetic decongestants. It works by reducing congestion in the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, nasal passages and sinuses, and making it easier to breathe.
Chlorphenamine belongs to a group of medicines called 'antihistamines' Antihistamines help reduce allergic symptoms by preventing the effects of a substance called histamine. Histamine is produced by the body in response to foreign substances that the body is allergic to.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you have any questions about this medicine. Your pharmacist or doctor may have given it for another reason.
This medicine is only available from a pharmacist.
Before you take PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE
When you must not take it
Do not take PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE tablets if you have an allergy to:
- Any medicine containing paracetamol, pseudoephedrine, or chlorphenamine or other antihistamines.
- Any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- Shortness of breath;
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing;
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or other parts of the body;
- Rash, itching or hives on the skin.
Do not take this medicine if you have:
- Very high blood pressure;
- Severe coronary artery disease (heart disease caused by poor blood flow or narrowing of the blood vessels of the heart);
- Taken monoamine oxidase inhibitors, medicines used to treat depression, in the last 14 days.
Do not take this medicine if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions:
- Glaucoma (high pressure in the eyes);
- Stomach or duodenal ulcer, or other stomach problem;
- Prostate problems;
- Bladder problems.
Do not take this medicine if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It may affect your developing baby if you take it during pregnancy. Your pharmacist or doctor will discuss the benefits and possible risks of taking the medicine during pregnancy.
Do not take this medicine if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It passes into the breast milk and there is a possibility that the baby may be affected.
Do not give this medicine to newborn or premature babies.
Do not take this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
If you are not sure whether you should start taking this medicine, talk to your pharmacist or doctor.
Before you start to take it
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods preservatives or dyes.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you have or have had any of the following medical conditions:
- High blood pressure;
- Overactive thyroid gland;
- Diabetes;
- Heart disease and poor blood flow in the blood vessels of the heart;
- Glaucoma (high pressure in the eyes);
- Prostate problems;
- Liver or kidney disease;
- Epilepsy.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you take sedatives.
If you have not told your pharmacist or doctor about any of the above, tell him/her before you start taking PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE.
Taking other medicines
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you get without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE may interfere with each other. These include:
- Warfarin, a medicine used to prevent blood clots;
- Metoclopramide, a medicine used to control nausea and vomiting;
- Medicines such as phenytoin used to treat epilepsy or fits;
- Chloramphenicol, an antibiotic used to treat ear and eye infections;
- Medicines used to treat depression, especially monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants;
- Medicines used to treat heart conditions;
- Medicines used to treat high blood pressure;
- Medicines used to treat urinary tract infections and bladder problems;
- Medicines used to treat behavioural disorders;
- Phenylephrine, a medicine used to treat congestion;
- Appetite suppressants;
- Medicines used to help you sleep or relax (sedatives and hypnotics);
- Opioid analgesics, medicines used to treat pain;
- Alcohol.
These medicines may be affected by PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines. Your pharmacist and doctor will have more information on these and other medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
How to take PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE
Follow all directions given to you by your pharmacist or doctor carefully.
They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the carton or in this leaflet, ask your ask your pharmacist or doctor for help.
How much to take
Adults and children over 12 years: Two tablets every 4 to 6 hours when necessary. No more than 4 doses should be taken in 24 hours.
Do not give to children under 12 years of age.
If you are over 65 years of age, talk to your pharmacist or doctor about how much to take.
Elderly patients are more likely to have side effects from taking these medicines.
How to take it
Take tablets as required with water.
When to take it
Take tablets every 4 to 6 hours as required.
How long to take it
Do not take this medicine for longer than a few days at a time (adults) or 48 hours at a time (children over 12 years) unless advised to by a doctor.
If you forget to take it
If it is less than 4 hours before your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to.
Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember, and then go back to taking your medicines as you would normally. Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed. This may increase the chance of you getting unwanted side effects.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your pharmacist or doctor. If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (in Australia call 13 11 26; in New Zealand, call 0800 764 766) for advice, or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are taking PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE
Things you must do
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor if your symptoms do not improve. Your pharmacist or doctor will assess your condition and decide if you should continue to take the medicine.
Things you must not do
Children over 12 years of age: Do not take this medicine for more than 48 hours unless a doctor has told you to.
Do not give to children under 12 years of age.
Adults: Do not take for more than a few days at a time unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not take more than the recommended dose unless your pharmacist or doctor tells you to.
Do not take PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE tablets to treat any other complaints unless your pharmacist or doctor tells you to.
Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not drink alcohol while taking PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE.
The sedation effects of alcohol may be increased.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how the medicine affects you. This medicine may cause dizziness or sleepiness in some people. If this happens, do not drive, use or operate machinery.
Pseudoephedrine may cause sleeplessness if it is taken up to several hours before going to bed.
Side effects
Tell your pharmacist or doctor as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE.
This medicine helps most people with the temporary relief from the symptoms of sinus pain, headache, nasal congestion and symptoms of fever and hayfever, but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people.
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not.
You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following list of side effects. You may not experience any of them. Ask your pharmacist or doctor to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- Nausea or dyspepsia;
- Difficulty sleeping;
- Nervousness and irritability;
- Excitability;
- Restlessness;
- Dizziness;
- Fear or anxiety;
- Fast or rapid heart beat;
- Tremors;
- Hallucinations;
- Drowsiness or sleepiness;
- Dry mouth, nose and throat;
- Constipation;
- Twitching or jerking muscles.
The above list includes the more common side effects of your medicine. They are usually mild and short lived. Children and people over 65 years of age may have an increased chance of getting side effects.
Tell your doctor as soon as possible if you notice any of the following:
- Difficult or painful urination;
- Seizures (fits).
The above list includes serious side effects that may require medical attention. These side effects are rare.
If any of the following happen, tell your pharmacist or doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- Urine retention;
- Shortness of breath;
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing;
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body;
- Rash, itching or hives on the skin.
The above list includes very serious side effects.
You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation.
These side effects are very rare for low doses of this medicine and when used for a short period of time.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
After taking PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE
Storage
Keep your medicine in the original pack until it is time to take it.
Keep your medicine in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C.
Do not store PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink.
Do not leave it on a window sill or in the car. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it.
A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
Ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over, or if the expiry date has passed.
Product description
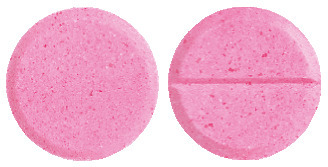
What it looks like
This medicine is sold in a carton with a blister pack containing 24 tablets.
The tablets are pink and round with breakline.
Ingredients
PHARMACY ACTION Hayfever & Sinus Pain Relief PSE tablets contain 500 mg of paracetamol, 30 mg of pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and 2 mg of chlorphenamine maleate as the active ingredients.
It also contains:
- Microcrystalline cellulose;
- Crospovidone;
- Erythrosine (dye);
- Magnesium stearate;
- Povidone;
- Pregelatinised maize starch;
- Stearic acid.
This medicine does not contain gluten, aspirin, salt, sugar, lactose, preservatives or yeast.
Australian Registration Numbers
AUST R 189868.
Sponsor
Generic Health Pty Ltd
Suite 2, Level 2
19-23 Prospect Street
Box Hill, VIC, 3128
Australia
E-mail: [email protected]
Telephone: +61 3 9809 7900
Website: www.generichealth.com.au
This leaflet was prepared in September 2020.
Published by MIMS January 2021