What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Phenergan.
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your pharmacist or doctor.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your pharmacist or doctor has weighed the risks of you taking Phenergan against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What Phenergan is used for
Phenergan is an antihistamine used to treat a number of conditions:
- allergies - allergic contact dermatitis, hives, hayfever, bites and stings
- respiratory symptoms due to allergies - runny nose
- nausea and vomiting - motion sickness
- assists in the management of the symptoms of chicken pox and measles by acting as a sedative
- for short-term use for sedation on the advice of a pharmacist or doctor - do not use for more than 7-10 days.
Antihistamines help reduce allergic symptoms by preventing the effects of a substance called histamine. Histamine is produced by the body in response to foreign substances that the body is allergic to.
Your pharmacist or doctor may have recommended Phenergan for another reason.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you have any questions about this medicine.
Phenergan must not be used in children under 2 years of age, due to the potential for fatal respiratory depression.
This medicine may affect your ability to drive a car or operate machinery.
Before you take it
When you must not take it
Do not take Phenergan if you have an allergy to:
- any medicine containing promethazine hydrochloride
- any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
Do not take Phenergan if you are also taking or have recently (within the last 14 days) taken monoamine oxidase inhibitors, a type of medicine used to treat depression.
Do not take Phenergan if you have jaundice.
Do not take this medicine if you are receiving or have received high doses of other CNS depressant medications (for example, drugs that are used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders).
Do not take this medicine if you have slowed breathing or heart rate of any cause.
Any person who is unconscious or in a coma must not be treated with Phenergan.
Do not give Phenergan to newborn or premature babies.
Do not use for children less than two years of age, due to the potential for fatal respiratory depression.
Do not take Phenergan if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It may affect your developing baby if you take it during pregnancy. Your pharmacist or doctor will discuss the benefits and possible risks of taking the medicine during pregnancy.
Do not take Phenergan if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It passes into the breast milk and there is a possibility that the baby may be affected.
Do not take Phenergan after the expiry date (EXP) printed on the pack. If you take this medicine after the expiry date has passed, it may not work as well.
Do not take Phenergan if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
Before you start to take it
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you have allergies to:
- any other medicines
- any other substances, such as foods, preservatives or dyes
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you have or have had any medical conditions, especially the following:
- kidney or liver disease
- epilepsy
- cardiovascular disease
- blood pressure problems
- bladder problems
- breathing problems
- glaucoma - an eye condition
- prostate problems
- stomach ulcer or blockage
Tell your doctor if you plan to have surgery.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you take sedatives.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant. Phenergan is not recommended for use during pregnancy. If there is a need to consider Phenergan during your pregnancy, your pharmacist or doctor will discuss with you the benefits and risks of taking it.
Do not take Phenergan if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It passes into the breast milk and there is a possibility that the baby may be affected.
Taking other medicines
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including any that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and Phenergan may interfere with each other. Phenergan may increase the sedative effect of some drugs. These include:
- medicines used to treat depression, especially monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants
- medicines used to help you sleep or relax (sedatives and hypnotics)
- opioid analgesics, medicines used to treat pain
- other antihistamines
- alcohol
These medicines may be affected by Phenergan or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines.
Your pharmacist and doctor will have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
How to take it
How much to take
Follow all directions given to you by your pharmacist or doctor carefully. They may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
Phenergan tablets are recommended for adults and children over 6 years of age.
Phenergan elixir is recommended for children 2-5 years of age.
It is recommended that the lowest effective dose of Phenergan be used in children 2 years of age or older.
Allergic Disorder
Adults: One to three 25mg tablets as a single dose at night, or one to two 10mg tablets, two to three times daily.
Children 6-12 years: One to two 10mg tablets, or 10 to 25mL of the elixir as a single dose at night, or one 10mg tablet, or 10mL of the elixir, two to three times daily.
Children 2-5 years: 5-15mL of elixir as a single dose at night, or 5mL of elixir, two to three times daily.
Sedation
For short term use on the advice of a pharmacist or doctor.
Adults: One to three 25mg tablets as a single dose at night.
Children 6-12 years: One to two 10mg tablets, or 10 to 25mL of the elixir, as a single dose at night.
Children 2-5 years: 5-15mL of elixir as a single dose at night.
Travel Sickness
Adults: One 25mg tablet.
Children 6-12 years: One 10mg tablet or 10mL of the elixir.
Children 2-5 years: 5mL of elixir.
To be taken the night before travel and repeated after 6 to 8 hours on the following day if required.
Nausea and Vomiting
Adults: One 25mg tablet every 4 to 6 hours to a maximum daily dose of four 25mg tablets.
Children 6-12 years: One 10mg tablet or 10mL of the elixir, every 4 to 6 hours to a maximum daily dose of two 10mg tablets or 25mL of the elixir.
Children 2-5 years: 5mL of elixir every 4 to 6 hours to a maximum daily dose of 15mL.
If you do not understand the instructions on the carton or the label, ask your pharmacist or doctor for help.
Do not take more than the recommended dose.
Use this drug only as recommended. Do not exceed the recommended dose. There have been case reports of promethazine abuse.
Use in the Elderly
If you are over 65 years of age, talk to you pharmacist or doctor about how much to take. Elderly patients are more likely to have side effects from taking these medicines.
How to take it
Tablets
Swallow Phenergan tablets whole with a full glass of water.
Elixir
Measure out the amount of elixir to be taken.
How long to take it
Phenergan should not usually be taken for more than 10 days in a row. If your symptoms persist, see your pharmacist or doctor for advice.
If you forget to take it
If you are taking Phenergan for an allergic disorder and you forget to take your bedtime dose, you may need to take your dose in two or three smaller doses during the following day.
Check with your pharmacist or doctor.
If you are taking Phenergan for travel sickness or nausea and vomiting, take your dose as soon as you remember.
If you are taking Phenergan for sedation, take your dose as soon as you remember. Be careful because you may still be affected in the morning.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed. This may be harmful.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your pharmacist or doctor.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (in Australia, call 13 11 26; in New Zealand, call 0800 764 766) for advice or go to Accident and Emergency at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much Phenergan.
Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
If you take too much Phenergan, you may experience:
Adults
- drowsiness
- convulsions and/or tremors
- difficulty breathing
- unconsciousness
- acute anxiety
- hallucinations
Children
- over - excitement
- shaky and unsteady movements
- convulsions and/or tremors
- hallucinations
- difficulty breathing
- unconsciousness
- high fever
While you are taking it
Things you must do
Phenergan may cause your skin to be more sensitive to the sun. You should protect your skin from exposure to bright sunlight.
Tell any other doctors, dentists, and pharmacists who are treating you that you are taking Phenergan.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, tell your pharmacist or doctor that you are taking Phenergan.
If you plan to have surgery that needs a general anaesthetic, tell your doctor or dentist that you are taking this medicine.
If you become pregnant while you are taking this medicine, stop taking it and tell your doctor immediately.
Talk to your pharmacist or doctor if your symptoms do not improve. Your pharmacist or doctor will assess your condition and decide if you should continue to take the medicine.
Things you must not do
Do not give Phenergan to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not take Phenergan to treat any other complaints unless your pharmacist or doctor tells you to.
Do not drink alcohol while taking Phenergan. The sedation effects of alcohol may be increased.
Do not take more than the recommended dose unless your pharmacist or doctor tells you to.
Things to be careful of
Phenergan is a known sedative and may cause drowsiness in some people. Make sure you know how you react to Phenergan before you drive a car, operate machinery, or do anything else that could be dangerous if you are drowsy. If this occurs do not drive or operate machinery.
If you have a single dose at bedtime, you may still be affected in the morning.
A very serious and sometimes deadly health problem called neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) may happen. Stop treatment and call your doctor right away if you have high fever, muscle cramps or stiffness, dizziness, very bad headache, fast heartbeat, confusion, agitation, hallucinations, or are sweating a lot.
Avoid alcohol.
Children and the elderly are especially sensitive to the effects of antihistamines.
Side effects
Phenergan may have unwanted side effects in some people. All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking Phenergan.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- dry mouth, nose & throat
- stomach upset
- loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
- diarrhoea or constipation
- tiredness or sleepiness
- restlessness
- blurred vision
- headache
- nightmares in children
- increased sensitivity of the skin to sun.
These are mild side effects of the medicine and are short-lived.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor immediately if you notice any of the following:
- fever
- difficulty breathing
- irregular heart beat
- jaundice - yellow tinge to skin or eyes
- tremors or convulsions
- tinnitus - buzzing, hissing, ringing or other persistent noise in the ears
- seizures (fits)
- hallucinations
- nervousness and irritability
- agitation
- anxiety
- twitching or jerking muscles
- muscle cramps or stiffness
- dizziness, lightheadedness
- severe headache
- confusion
- excessive sweating
- difficulty passing urine
The above list includes serious side effects that may require medical attention. Serious side effects are rare.
If any of the following happen, tell your doctor immediately or go to Accident and Emergency at your nearest hospital:
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- skin rashes
The above list includes very serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation. These side effects are very rare.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you notice anything that is making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may occur in some patients.
Do not be alarmed by the lists of possible side effects. You may not experience any of them.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor if you have any questions.
After taking Phenergan
Storage
Keep your medicine in the pack until it is time to take it. If you take your medicine out of the pack it will not keep as well.
Keep your tablets in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 30°C.
Keep your elixir in a cool dry place, protected from light, where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Do not store Phenergan or any other medicine in the bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave it in the car on hot days or on window sills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep it where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Disposal
If your pharmacist or doctor tells you to stop taking Phenergan or if it has passed the expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any left over.
What it looks like
Phenergan Tablets are available in two strengths:
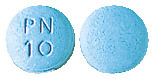
- 10mg - round and pale blue tablets, with 'PN 10' embossed on one side.
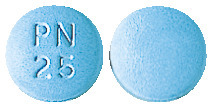
- 25mg - round and pale blue tablets, with 'PN 25' embossed on one side.
Both tablet strengths are available in blister packs of 50 tablets and 25 tablets (New Zealand only).
Phenergan Elixir is a clear, bright, golden, syrupy liquid. Phenergan elixir is available in a 100mL bottle.
Ingredients
Phenergan Tablets
Active ingredient:
- 10mg tablets - 10mg of promethazine hydrochloride per tablet
- 25mg tablets - 25mg of promethazine hydrochloride per tablet
Inactive ingredients:
The 10mg and 25mg tablets also contain:
- lactose
- starch maize
- povidone
- magnesium stearate
- hypromellose
- macrogol 200
- blue opaspray
Phenergan Elixir
Active ingredient:
Phenergan elixir contains 1mg/mL of promethazine hydrochloride.
Inactive ingredients:
Phenergan elixir also contains:
- maltitol solution
- acesulfame potassium
- sodium benzoate
- sodium citrate
- citric acid
- sodium sulfite
- sodium metabisulfite
- ascorbic acid
- caramel
- orange juice flavour
Sponsor
Phenergan Tablets and Elixir are supplied in Australia by:
sanofi-aventis australia pty ltd
12-24 Talavera Road
Macquarie Park NSW 2113
Phenergan Tablets and Elixir are supplied in New Zealand by:
sanofi-aventis new zealand limited
Level 8, James and Wells Tower
56 Cawley Street
Ellerslie
Auckland
Australian Registration Numbers:
Phenergan 10mg tablets
AUST R 80159
Phenergan 25mg tablets
AUST R 80160
Phenergan Elixir 1mg/mL
AUST R 61576
This leaflet was updated in March 2019.
(R)Registered Trademark
phenergan-ccsiv2-cmiv9-06may19
Published by MIMS July 2019