What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about SYMDEKO tablets.
It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking SYMDEKO against the benefits he/she expects it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with YOUR medicine. You may need to read it again.
What SYMDEKO is used for
SYMDEKO is used for the chronic treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 12 years and older who are homozygous for the F508del mutation or who have at least one mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene that is listed in the approved indication.
What is cystic fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis is caused by genetic defects that limit the flow of chloride and water through cell membranes.
As a result, the mucus in the lungs (and other organs) becomes thick and sticky, clogs the lungs and makes it easier for germs to grow. SYMDEKO is a medicine that works by improving the flow of chloride and water in patients with cystic fibrosis who have a certain genetic defect.
How SYMDEKO works
SYMDEKO belongs to a group of medicines called "cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators". SYMDEKO includes two types of tablets, one contains tezacaftor and ivacaftor (morning dose) and the other contains ivacaftor (evening dose).
Tezacaftor is a "CFTR corrector" and works to increase the amount of protein at the cell surface.
Ivacaftor is a "CFTR potentiator" that makes the protein work better once it reaches the cell surface.
SYMDEKO is not addictive.
Before you take SYMDEKO
When you must not take it
Do not take SYMDEKO if you have an allergy to:
- any medicine containing tezacaftor or ivacaftor (the active ingredients in SYMDEKO).
- any of the other ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin
Do not take this medicine after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If the medicine has expired or the packaging is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
Before you start to take it
Tell your doctor if you have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine. Your doctor will help you decide what is best for you or your child.
If you are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine. It is unknown whether SYMDEKO is excreted in human milk. If you plan to breast-feed, ask your doctor for advice before taking SYMDEKO.
Talk to your doctor before starting treatment if you have received an organ transplant.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including:
- all prescription medicines
- all medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements or natural therapies you buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket, naturopath or health food shop.
Some medicines may be affected by SYMDEKO or may affect how well it works. You may need different amounts of your medicines, or you may need to take different medicines. Your doctor will advise you.
Take SYMDEKO with fat-containing food and avoid food containing grapefruit or Seville oranges.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following:
- Antifungal medicines (used for the treatment of fungal infections):
- ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole - Antibiotic medicines (used for the treatment of bacterial infections):
- telithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, rifampicin, rifabutin - Anticonvulsant medicines (used for the treatment of epileptic seizures ):
- phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin - Herbal medicines:
- St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) - Benzodiazepines (used for the treatment of anxiety, insomnia, agitation, etc.):
- midazolam, alprazolam, diazepam, triazolam - Immunosuppressants (used after an organ transplantation):
- ciclosporine, everolimus sirolimus and tacrolimus - Cardiac glycosides (used for the treatment of mild to moderate congestive heart failure and an abnormal heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation):
- digoxin - Anticoagulants (used to prevent blood clots from forming or growing larger in blood and blood vessels):
- warfarin
Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or to avoid while taking SYMDEKO.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about this list of medicines.
Use in children
Do not give SYMDEKO to children under 12 years of age. The safety and efficacy of this medicine in children under 12 years of age have not been established.
Abnormality of the eye lens (cataract) without any effect on vision has been noted in some children receiving this treatment.
Your doctor may perform some eye examinations prior to and during the treatment with SYMDEKO.
Laboratory Testing
Your doctor will do some blood tests to check your liver prior to and while you are taking SYMDEKO, particularly during the first year and especially if you have had high liver enzymes in the past.
Talk to your doctor if you have been told you have liver or kidney disease or if you are taking any other medicine, as your doctor may need to adjust the dose of SYMDEKO.
Increased liver enzymes in the blood have been seen in some people receiving SYMDEKO. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms, which may be a sign of liver problems:
- pain or discomfort in the upper right stomach (abdominal) area
- yellowing of the skin or the white part of the eyes
- loss of appetite
- nausea or vomiting
- dark urine
How to take SYMDEKO
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor and pharmacist carefully. These directions may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
How much to take
Your doctor will tell you how much SYMDEKO you need to take each day. This may depend on your condition and whether or not you are taking any other medicines.
The usual dose of SYMDEKO is:
- One yellow tablet in the morning and;
- One blue tablet in the evening
If you have liver problems, your doctor may need to reduce the dose as your liver is not clearing ivacaftor and tezacaftor as fast as in people who do not have problems with liver function.
How to take it
SYMDEKO is for oral use.
Do not break, chew or dissolve the tablets.
Tablets
Take 1 yellow tablet (tezacaftor 100mg/ivacaftor 150mg) in the morning with a fat-containing meal or snack.
Take 1 blue tablet (ivacaftor 150 mg) about 12 hours later in the evening with a fat containing meal or snack.
Examples of meals or snacks that contain fat are those prepared with butter or oils or those containing eggs. Other fat-containing foods are:
- Cheese, whole milk, whole-milk dairy products, yogurt, chocolate
- Meats, oily fish
- Avocados, hummus, soy-based products (tofu)
- Nuts, fat-containing nutritional bars or drinks
How long to take it
Take SYMDEKO every day and continue taking it for as long as your doctor tells you. Your doctor will determine if your treatment should be stopped.
If you forget to take it
Take the missed dose if less than 6 hours have passed since the time you missed the dose. Otherwise, wait until your next scheduled dose as you normally would.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose that you missed. This may increase the chance of you getting an unwanted side effect.
If you are not sure what to do, talk to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you take too much (overdose)
Immediately telephone your doctor or the Poisons Information Centre (telephone Australia 13 11 26) for advice, or go to the Emergency Department at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much SYMDEKO. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You may need urgent medical attention.
While you are using SYMDEKO
Things you must do
Keep all of your doctor's appointments so that your progress can be checked.
Use SYMDEKO exactly how your doctor has prescribed.
Take SYMDEKO with fat-containing food and avoid food containing grapefruit or Seville oranges.
Tell all doctors, dentists, and pharmacists who are treating you that you are using SYMDEKO.
Tell your doctor if you become pregnant while using SYMDEKO.
Tell your doctor if, for any reason, you have not used SYMDEKO exactly as prescribed.
Things you must not do
Do not stop using SYMDEKO or change the dose without first checking with your doctor.
Do not let yourself run out of medicine over the weekend or on holidays.
Do not give SYMDEKO to anyone else even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not use SYMDEKO to treat other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
Do not take any other medicines whether they require a prescription or not without first telling your doctor or consulting a pharmacist.
Things to be careful of
Avoid food containing grapefruit or Seville oranges during treatment with SYMDEKO as they may increase the amount of SYMDEKO in your body.
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how SYMDEKO affects you.
SYMDEKO can make you dizzy. Do not drive or use machines unless you are sure that you are not affected.
If your child is taking SYMDEKO it is advised that he/she does not ride his/her bike or do anything else that needs his/her full attention unless you are sure that your child is not affected.
SYMDEKO contains lactose. If you have been told by your doctor that you have intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
Side effects
Tell your doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you do not feel well while you are taking SYMDEKO.
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical treatment if you get some of the side effects.
Ask your doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell your doctor if …
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
Very common side effects
(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- Headache
- Throat and nose infections
Common side effects
(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Feeling sick (nausea)
- Sinus congestion
- Dizziness
Go to hospital if …
Tell your doctor immediately or go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital if you notice any of the following:
- significant pain or discomfort in the upper right stomach (abdominal) area
- yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes
These may be indicative of serious side effects. You may need urgent medical attention. Serious side effects are uncommon.
This is not a complete list of all possible side effects. Your doctor or pharmacist has a more complete list. Others may occur in some people and there may be some side effects not yet known.
Tell your doctor if you notice anything else that is making you feel unwell, even if it is not on this list. Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
After taking SYMDEKO
Storage
Store below 30°C. Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop using SYMDEKO or SYMDEKO has passed its expiry date, ask your pharmacist what to do with any tablets that are left over.
Product description
Availability
SYMDEKO tablets are available in the following pack sizes:
- blister pack containing 56 filmcoated tablets (28 tablets containing both tezacaftor and ivacaftor (morning dose) and 28 tablets containing ivacaftor (evening dose)).
SYMDEKO tablets are available in the following strength:
- Tezacaftor 100mg/ivacaftor 150 mg and;
- Ivacaftor 150mg
What does SYMDEKO look like
Morning dose
Yellow, capsule-shaped tablet debossed with "V100" on one side and plain on the other (15.9 mm x 8.5 mm).
Evening dose
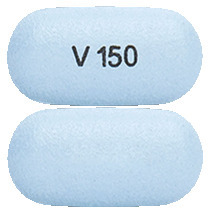
Light blue, capsule-shaped tablet, printed with "V150" in black ink on one side and plain on the other (16.5 mm x 8.4 mm).
Ingredients
Active ingredients
Morning Dose
- tezacaftor
- ivacaftor
Evening Dose
- ivacaftor
Inactive ingredients
Morning Dose
- Hypromellose acetate succinate
- Sodium lauryl sulfate
- Hypromellose
- Microcrystalline cellulose
- Croscarmellose sodium
- Magnesium stearate
- Opadry complete film coating system 20A120010 Yellow (PI No. 111630)
Evening Dose
- Microcrystalline cellulose Lactose monohydrate Hypromellose acetate succinate
- Croscarmellose sodium
- Sodium lauryl sulfate
- Silicon dioxide
- Magnesium stearate
- Carnauba wax
- Opadry II complete film coating system 85F90614 Blue (PI# 108371)
- OPACODE monogramming ink S-1-17823 BLACK (PI# 12108)
Sponsor
Vertex Pharmaceuticals (Australia) Pty Ltd
Suite 3, Level 3
601 Pacific Highway
St Leonards
NSW 2065
Australia
Telephone: 1800 179 987
ARTG Number
AUST R 298329
This leaflet was prepared
5 March 19
©2019 Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
SYMDEKO, VERTEX and the VERTEX triangle logo are registered trademarks of Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated.
Published by MIMS May 2019





 The morning and evening dose should be taken with fat-containing food, approximately 12 hours apart.
The morning and evening dose should be taken with fat-containing food, approximately 12 hours apart.


 Safety data from the following additional studies are consistent with the safety data from the placebo-controlled Phase 3 studies (Studies 106 (EVOLVE), 108 (EXPAND) and 107):
Safety data from the following additional studies are consistent with the safety data from the placebo-controlled Phase 3 studies (Studies 106 (EVOLVE), 108 (EXPAND) and 107): At Week 24 the proportion of patients who remained free from pulmonary exacerbations was significantly higher for patients treated with Symdeko compared with placebo. The rate ratio of exacerbations through Week 24 in patients treated with Symdeko was 0.65 (95% CI: 0.48, 0.88; P = 0.0054), representing a reduction relative to placebo of 35% (see Figure 1).
At Week 24 the proportion of patients who remained free from pulmonary exacerbations was significantly higher for patients treated with Symdeko compared with placebo. The rate ratio of exacerbations through Week 24 in patients treated with Symdeko was 0.65 (95% CI: 0.48, 0.88; P = 0.0054), representing a reduction relative to placebo of 35% (see Figure 1). BMI increased in both treatment groups in EVOLVE (Symdeko: 0.18 kg/m2, placebo: 0.12 kg/m2). The treatment difference of 0.06 kg/m2 mean change in BMI from baseline to Week 24 (95% CI: -0.08, 0.19) in EVOLVE was not statistically significant.
BMI increased in both treatment groups in EVOLVE (Symdeko: 0.18 kg/m2, placebo: 0.12 kg/m2). The treatment difference of 0.06 kg/m2 mean change in BMI from baseline to Week 24 (95% CI: -0.08, 0.19) in EVOLVE was not statistically significant.

 After 96 weeks of Symdeko treatment in EXTEND (Study 110), the absolute change from baseline in BMI for subjects who received placebo in EVOLVE (Study 106) was 0.47 (95% CI: 0.30, 0.65), and for patients who received Symdeko in EVOLVE (Study 106) was 0.38 (95% CI: 0.20, 0.55). After 96 weeks of Symdeko treatment in EXTEND (Study 110), the absolute change from baseline in BMI for subjects who received placebo in EXPAND (Study 108) was 1.07 (95% CI: 0.59, 1.55), for patients who received Symdeko in combination with ivacaftor in Study 108 was 0.96 (95% CI: 0.45, 1.47), and for patients who received Symdeko was 1.05 (95% CI: 0.56, 1.55).
After 96 weeks of Symdeko treatment in EXTEND (Study 110), the absolute change from baseline in BMI for subjects who received placebo in EVOLVE (Study 106) was 0.47 (95% CI: 0.30, 0.65), and for patients who received Symdeko in EVOLVE (Study 106) was 0.38 (95% CI: 0.20, 0.55). After 96 weeks of Symdeko treatment in EXTEND (Study 110), the absolute change from baseline in BMI for subjects who received placebo in EXPAND (Study 108) was 1.07 (95% CI: 0.59, 1.55), for patients who received Symdeko in combination with ivacaftor in Study 108 was 0.96 (95% CI: 0.45, 1.47), and for patients who received Symdeko was 1.05 (95% CI: 0.56, 1.55). In subgroup analyses of F/F and F/RF patients, the within group mean absolute change in LCI2.5 was -0.39 (95% CI: -0.67, -0.10) and -0.92 (95% CI: -1.65, -0.20), respectively. The within group mean change in CFQ-R respiratory domain scores in F/F and F/RF patients was 1.4 points (95% CI: -1.9, 4.7) and 5.6 points (95% CI: -2.8, 13.9), respectively. Growth parameters remained stable over 8 weeks of Symdeko treatment.
In subgroup analyses of F/F and F/RF patients, the within group mean absolute change in LCI2.5 was -0.39 (95% CI: -0.67, -0.10) and -0.92 (95% CI: -1.65, -0.20), respectively. The within group mean change in CFQ-R respiratory domain scores in F/F and F/RF patients was 1.4 points (95% CI: -1.9, 4.7) and 5.6 points (95% CI: -2.8, 13.9), respectively. Growth parameters remained stable over 8 weeks of Symdeko treatment.

 Tezacaftor: 1-(2,2-difluoro-2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-{1-[(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]-6-fluoro-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropan-2-yl)-1Hindol-5-yl} cyclopropane-1-carboxamide.
Tezacaftor: 1-(2,2-difluoro-2H-1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-{1-[(2R)-2,3-dihydroxypropyl]-6-fluoro-2-(1-hydroxy-2-methylpropan-2-yl)-1Hindol-5-yl} cyclopropane-1-carboxamide. Ivacaftor: N‑(2,4‑di‑tert‑butyl‑5‑hydroxyphenyl)‑4‑oxo‑1,4‑dihydroquinoline‑3‑carboxamide.
Ivacaftor: N‑(2,4‑di‑tert‑butyl‑5‑hydroxyphenyl)‑4‑oxo‑1,4‑dihydroquinoline‑3‑carboxamide.