What is in this leaflet
This leaflet answers some common questions about Zyvox. It does not contain all the available information. It does not take the place of talking to your or your child's doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you or your child taking Zyvox against the expected benefits it will have.
If you have any concerns about you or your child taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
What Zyvox is used for
Zyvox contains the active ingredient linezolid.
Linezolid is an antibiotic (an agent used to destroy certain types of bacteria). It is used in the treatment of bacterial infections such as pneumonia, skin infections or blood infections.
Depending on the type of bacteria, you may be given additional medicines.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why Zyvox has been prescribed for you or your child. Your doctor may have prescribed it for another reason.
This medicine is not addictive.
Before treatment with Zyvox
When Zyvox must not be used
Zyvox must not be given if you or your child:
- are allergic to linezolid or any of the other ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
Some of the symptoms of an allergic reaction may include: shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body, rash, itching or hives on the skin. - have uncontrolled high blood pressure
- have pheochromocytoma (a type of tumour of the adrenal gland)
- have thyrotoxicosis (an overactive thyroid gland)
- have flushing or other symptoms caused by a carcinoid tumour
- are taking or have taken in the last two weeks any medicine that is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (e.g. moclobemide, phenelzine or tranylcypromine to treat depression or selegiline to treat Parkinson's disease)
- are taking any medicine that is an SSRI or serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, which are types of medicine to treat depression, anxiety, panic attacks, obsessive-compulsive disorders or obesity (e.g. citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, duloxetine, sibutramine, venlafaxine)
- tricyclic antidepressants, which are medicines to treat depression (e.g. amitriptyline, clomipramine, dothiepin, doxepin, imipramine, nortriptyline, trimipramine)
- buspirone, a medicine to treat anxiety
- some medicines to treat migraine (e.g. naratriptan, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan)
- pethidine, a medicine to treat pain
- any cold or flu medicine containing pseudoephedrine
- adrenaline, a medicine used to treat severe allergic reactions
- any other medicine that increases blood pressure (e.g. noradrenaline, dopamine, dobutamine).
Do not use Zyvox after the expiry date printed on the pack or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering. If it has expired or is damaged, return it to your pharmacist for disposal.
Do not use Zyvox oral suspension if it is more than 3 weeks since you received it from the pharmacist.
If you are not sure whether you or your child should start taking this medicine, talk to your doctor.
Before treatment with Zyvox
Tell your doctor if you or your child have allergies to any other medicines, foods, preservatives or dyes.
Tell the doctor if you or your child:
- have diarrhoea
- have phenylketonuria
- Zyvox oral suspension contains aspartame and this is partly converted into phenylalanine.
- are anaemic or have had any abnormal blood test results (e.g. low haemoglobin or platelets)
- are diabetic.
Zyvox injection contains glucose.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breast-feeding. Your doctor can discuss with you the risks and benefits involved.
If you have not told your doctor about any of the above, tell them before you or your child start taking Zyvox.
Taking other medicines
Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines, including medicines that you buy without a prescription from a pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Some medicines and Zyvox may interfere with each other.
These include:
- any medicine that inhibits monoamine oxidase (e.g. moclobemide, phenelzine or tranylcypromine to treat depression or selegiline to treat Parkinson's disease)
- are taking any medicine that is an SSRI or serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, which are types of medicine to treat depression, anxiety, panic attacks, obsessive-compulsive disorders or obesity (e.g. citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, duloxetine, sibutramine, venlafaxine)
- tricyclic antidepressants, which are medicines to treat depression (e.g. amitriptyline, clomipramine, dothiepin, doxepin, imipramine, nortriptyline, trimipramine)
- buspirone, a medicine to treat anxiety
- some medicines to treat migraine (e.g. naratriptan, sumatriptan, zolmitriptan)
- any medicine that is an opioid, a medicine to treat pain
- any cold or flu medicine containing pseudoephedrine
- adrenaline, a medicine used to treat severe allergic reactions
- any other medicine that increases blood pressure (e.g. noradrenaline, dopamine, dobutamine)
- rifampicin, a medicine to treat tuberculosis and some other infections
- any medicine that could reduce the levels of haemoglobin (the pigment in red blood cells which carries oxygen) or platelets (blood cells which help blood to clot).
These medicines may be affected by Zyvox or may affect how well it works. You or your child may need different amounts of medicines, or may need to take different medicines.
Your doctor and pharmacist have more information on medicines to be careful with or avoid while taking this medicine.
Tell the doctor if your or your child's diet contains a lot of mature cheese, yeast extracts, meat extracts, soya bean extracts (e.g. soy sauce), draught beers or wine. Zyvox may react with a substance which is naturally present in these foods.
How Zyvox is given
It is recommended that treatment with Zyvox begin in a hospital.
Tablets and Oral Suspension
Follow all directions given by your or your child's doctor carefully. These directions may differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the box, ask the doctor or pharmacist for help.
Gently mix Zyvox oral suspension by slowly turning the bottle over a few times before you use it. DO NOT SHAKE THE BOTTLE.
Do not take or give Zyvox oral suspension to your child if it is more than 3 weeks since you received it from your pharmacist.
Injection
Zyvox injection will be given to you or your child by the doctor or nurse.
Zyvox is a liquid which is given by slow injection into the blood (known as an intravenous infusion or "drip").
If you or your child is on dialysis, Zyvox infusion should be given after dialysis.
You or your child may be changed from Zyvox injection to Zyvox tablets or Zyvox oral suspension) to complete your course of treatment.
When to take it
Zyvox can be taken before, during or after meals.
If you or your child is on dialysis, take Zyvox after dialysis.
How much is given
Tablets
The recommended dose for adults and adolescents 12 years and older is one 600 mg tablet twice daily (every 12 hours).
Oral suspension
The recommended dose for babies and children up to 12 years of age is 10 mg/kg three times daily (every 8 hours).
The recommended dose for adults and adolescents 12 years and older is 30 mL (600 mg) twice daily.
Continue taking Zyvox until you or your child finish the tablets or oral suspension unless your doctor recommends otherwise.
Do not stop taking Zyvox unless your doctor tells you to, even if you feel better.
Do not stop giving Zyvox to your child unless your child's doctor tells you to, even if your child feels better. If you or your child do not complete the full course prescribed by the doctor, the bacteria causing the infection may continue to grow and multiply. The infection may not clear completely or it may return.
A course of treatment usually lasts 10 to 14 days but may be up to 28 days.
Injection
The recommended dose for adults and adolescents 12 years and older is 600 mg twice daily (every 12 hours).
The recommended doses for babies and children up to 12 years of age is 10 mg/kg three times daily (every 8 hours).
These doses are given intravenously by a "drip" over a period of 30 to 120 minutes.
Treatment is usually given every day for 10 to 14 days but may given for up to 28 days.
Ask the doctor if you want more information about the dose of Zyvox and how it is given.
In case of overdose
Immediately telephone your doctor or pharmacist or Poisons Information Centre on 13 11 26, or go to the Emergency department at the nearest hospital, if you think that you or anyone else may have been given too much Zyvox. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. You or your child may need urgent medical attention.
Symptoms of an overdose are vomiting, tremors (shaking), unsteadiness or lack of coordination.
While being treated with Zyvox
Things you must do
If you or your child are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor and pharmacist that you or your child are taking Zyvox.
Tell any other doctors, dentists and pharmacists who are treating you or your child that you are taking Zyvox.
If you or your child are going to have surgery, tell the surgeon or anaesthetist that you or your child are taking this medicine. It may affect other medicines used during surgery.
If you become pregnant while you are being treated with Zyvox, tell your doctor immediately.
Keep all of your doctor's appointments so that your or your child's progress can be checked. Your doctor may do some blood tests from time to time to make sure the medicine is working and to prevent unwanted side effects.
If the symptoms of the infection do not improve within a few days, or if they become worse, tell your or your child's doctor. As part of the treatment, you or your child may be given other medicines including other antibiotics. It is important to keep taking these medicines as well as Zyvox unless you are told otherwise by your doctor or pharmacist.
It is important to tell the doctor if you develop diarrhoea during or after treatment with Zyvox. Do this even if it occurs several weeks after Zyvox has been stopped.
Do not take any medicine to treat diarrhoea without first checking with the doctor. Diarrhoea may be caused by a serious condition affecting the bowel. You or your child may need urgent medical care.
If you or your child get a sore white mouth or tongue during or soon after treatment with Zyvox tell your doctor.
Tell the doctor if you or your child get vaginal itching or discharge. This may mean you or your child have a fungal infection called thrush. Sometimes the use of Zyvox allows fungi to grow which causes the symptoms described above. Zyvox does not work against fungi.
Things you must not do
Do not take Zyvox to treat other complaints unless your doctor tells you to do so.
Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
Do not stop taking your medicine or lower the dosage without checking with your doctor. If you stop taking it suddenly, your condition may worsen.
Do not start taking any other medicines, prescription or not, without first telling your doctor or pharmacist.
Do not give your child any other medicines, prescription or purchased from a health food shop, pharmacy or supermarket without first telling your doctor or pharmacist.
Do not take any medicine to treat diarrhoea without first checking with the doctor. Diarrhoea may be caused by a serious condition affecting the bowel. You or your child may need urgent medical care.
Avoid eating too much mature cheese, yeast extracts, meat extracts or soya bean extracts (e.g. soy sauce). Avoid drinking alcohol, especially draught beers and wine. This is because Zyvox may react with a substance which is naturally present in these foods.
If you or your child develop a throbbing headache after eating, tell your doctor or health care professional.
Things to be careful of
Be careful driving or operating machinery until you know how Zyvox affects you. This medicine may cause dizziness and visual impairment in some people. If you have any of these symptoms, do not drive, operate machinery or do anything else that could be dangerous. Children should be careful performing activities requiring attention such as riding bicycles or climbing.
Side effects
Tell the doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible if you or your child do not feel well while you are being treated with Zyvox.
This medicine helps most people, but it may have unwanted side effects in a few people. All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time they are not. You may need medical attention if you get some of the side effects.
Do not be alarmed by the following lists of side effects. You or your child may not experience any of them.
Ask the doctor or pharmacist to answer any questions you may have.
Tell the doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following and they worry you:
- headache
- sore, white mouth or tongue (oral thrush)
- vaginal itching or discharge (vaginal thrush)
- pain, cramping or bloating of the abdomen
- nausea or vomiting
- metallic taste
- change in the colour of the tongue
- change in the colour of teeth. This may be reversible
- headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls (these symptoms may indicate low sodium levels in the blood).
Tell your doctor immediately and before you or your child are given the next dose of Zyvox if you notice any of the following:
- skin reactions (hives, rash or itching)
- visual disturbances or numbness or weakness of the arms and legs (rare side effects that have been primarily reported in patients treated for longer than 28 days)
- tiredness, headaches, being short of breath when exercising, dizziness, looking pale, dark circles around the eyes, fever and chills, sore throat or bruising (these symptoms may indicate a decrease in the level of your blood cells)
- sweating, feeling drunk and dizzy, muscle twitching, fever and shivering, confusion
These may be symptoms of the serotonin syndrome, which is a rare but serious side effect.
If any of the following happen, tell your or your child's doctor immediately or go to the Emergency department at your nearest hospital:
- seizure
- hallucination
- fainting
- coma
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, severe itching or hives or blisters on the skin and bleeding in the lips, eyes, mouth, nose and genitals.
- painful red/purple spots with/without blisters and peeling of skin. This may be accompanied by fevers and chills, aching muscles, joint pain, enlarged lymph nodes and generally feeling unwell.
These may be signs of a serious allergic reaction or side effect. You or your child may need urgent medical attention or hospitalisation. These side effects are rare.
After stopping your treatment
Tell your or your child's doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of the following side effects, particularly if they occur several weeks after stopping treatment with Zyvox:
- severe stomach cramps
- watery and severe diarrhoea (which may be bloody), fever, in combination with one or both of the above.
Zyvox can cause some bacteria, which are normally present in the bowel and normally harmless, to multiply and therefore cause the above symptoms. You may need urgent medical attention.
Tell your or your child's doctor if you notice anything that is making you or your child feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed above may also occur in some people.
After using Zyvox
Storage
Keep your tablets or oral suspension in the original packaging, including outer carton, until it is time to take them. Keep oral suspension bottles tightly closed. If you take the medicine out of the pack it may not keep well.
Keep Zyvox tablets and Zyvox oral suspension in a cool dry place where the temperature stays below 25°C.
Do not store Zyvox or any other medicines in a bathroom or near a sink.
Do not leave it in the car or on window sills. Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep Zyvox where children cannot reach it. A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Zyvox injection will normally be stored in a hospital. It should be stored below 25°C and should be protected from light (kept in the box and foil wrapping before use).
Hospital staff will make sure the medicine is not used after the expiry date printed on the bag.
Disposal
If your doctor tells you to stop taking this medicine or the expiry date has passed, ask your pharmacist what to do with any medicine that is left over.
Product description
What it looks like
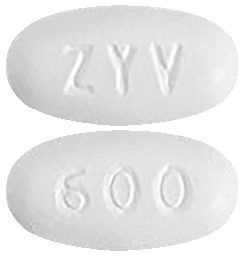
Zyvox tablets are white to off-white coated tablet with "ZYV" debossed on one side and "600" debossed on the other. The tablets are available in blister packs of 10 tablets.
Zyvox oral suspension is a white to yellow-orange fluid which is orange flavoured. It is supplied in an amber glass bottle with a screw cap. A measuring spoon with 2.5 mL and 5 mL markings is also provided.
Zyvox injection is a sterile, clear, colourless to yellow fluid for injection supplied as 300 mL in infusion bags. Each bag is for single use only and is packaged in a foil overwrap contained within an outer carton.
Ingredients
The active ingredient in Zyvox is linezolid.
Zyvox tablets contain 600 mg of linezolid.
The tablets also contain:
- microcrystalline cellulose (E460i)
- maize starch
- sodium starch glycollate
- hyprolose (E463)
- magnesium stearate (E572).
The film coating contains:
- hypromellose (E464)
- titanium dioxide (E171)
- macrogol 400
- carnauba wax (E903).
Zyvox oral suspension contains 20 mg/mL of linezolid (total 150 mL).
Other ingredients are:
- sucrose
- mannitol (E421)
- microcrystalline cellulose (E460i)
- carmellose sodium (E466)
- aspartame (E951)
- colloidal anhydrous silica (E551)
- sodium citrate dihydrate (E331)
- xanthan gum (E415)
- sodium benzoate (E211)
- citric acid (E330)
- sodium chloride.
The granules are flavoured with Mafco magnasweet, orange flavour, orange cream flavour, Sweet-am powder, vanilla flavour and peppermint flavour.
Important information about some of the ingredients in Zyvox oral suspension
This medicine contains
- aspartame, which is partly converted into phenylalanine.
- sodium benzoate is known to be a mild irritant to the skin, eyes and mucous membranes. In the quantities present in Zyvox suspension (0.2%) no harmful effects are expected.
- sodium may be harmful in a low-sodium diet. Each mL contains sodium as sodium citrate dihydrate (3 mg), sodium benzoate (2 mg) and sodium chloride (2.7 mg).
- Each mL contains 210.6 mg sucrose, 100 mg mannitol (E421) and 7 mg aspartame (E951). Fructose and sorbitol (E420) are present in mafco magna sweet (12 mg) and sweet-am powder (6 mg).
Zyvox is not suitable for treating people with hereditary fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency.
Sucrose may cause gastrointestinal complaints and diarrhoea.
Zyvox injection contains 2 mg/mL of linezolid.
Other ingredients are:
- glucose monohydrate
- sodium citrate dihydrate (E331)
- citric acid (E330)
- hydrochloric acid (E507)/sodium hydroxide (E524)
- water for injections.
Each mL of Zyvox solution of injection contains 50.24 mg glucose monohydrate and sodium as sodium citrate dihydrate (1.64 mg).
Supplier
Zyvox is supplied in Australia by:
Pfizer Australia Pty Ltd
Sydney, NSW
Toll Free Number: 1800 675 229.
www.pfizer.com.au
Australian Registration Number
600 mg tablets: AUST R 79694
20 mg/mL oral suspension: AUST R 79695
600 mg/300 mL injection: AUST R 79690
® = Registered Trademark
© Copyright
This leaflet was prepared in August 2021.
Published by MIMS October 2021



 Changes observed in laboratory parameters (without regard to drug relationship) generally reflected resolution of the infection, were not clinically significant, did not lead to discontinuation of therapy and were reversible. The incidence of patients with at least one substantially abnormal haematologic or serum chemistry value is presented in Table 4.
Changes observed in laboratory parameters (without regard to drug relationship) generally reflected resolution of the infection, were not clinically significant, did not lead to discontinuation of therapy and were reversible. The incidence of patients with at least one substantially abnormal haematologic or serum chemistry value is presented in Table 4.
 In a study of severely ill, hospitalised paediatric patients ranging in age from birth through 11 years, the percentage of patients who developed a substantially low platelet count was 12.9% with Zyvox and 13.4% with vancomycin. In an outpatient study of paediatric patients aged from 5 through 17 years, the percentage of patients who developed a substantially low platelet count was 0% with Zyvox and 0.4% with cefadroxil. Other changes observed in laboratory parameters, were not clinically significant, did not lead to discontinuation of therapy and were reversible. The incidence of paediatric patients with at least one substantially abnormal haematologic or serum chemistry value is presented in Table 6.
In a study of severely ill, hospitalised paediatric patients ranging in age from birth through 11 years, the percentage of patients who developed a substantially low platelet count was 12.9% with Zyvox and 13.4% with vancomycin. In an outpatient study of paediatric patients aged from 5 through 17 years, the percentage of patients who developed a substantially low platelet count was 0% with Zyvox and 0.4% with cefadroxil. Other changes observed in laboratory parameters, were not clinically significant, did not lead to discontinuation of therapy and were reversible. The incidence of paediatric patients with at least one substantially abnormal haematologic or serum chemistry value is presented in Table 6.
 The studies used to define the above breakpoints employed standard NCCLS (National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards) microdilution and agar diffusion methods.
The studies used to define the above breakpoints employed standard NCCLS (National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards) microdilution and agar diffusion methods.





 As can be seen from Table 14, average Cmin values achieved in plasma using the 600 mg bid dosage regimen approximate to the highest MIC90 (4 microgram/mL) for the least susceptible microorganisms.
As can be seen from Table 14, average Cmin values achieved in plasma using the 600 mg bid dosage regimen approximate to the highest MIC90 (4 microgram/mL) for the least susceptible microorganisms.
 The chemical name is (S)-N-[[3-[3-fluoro-4-(4-morpholinyl) phenyl]-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl] methyl]-acetamide. The empirical formula of linezolid is C16H20FN3O4 and the molecular weight of 337.35.
The chemical name is (S)-N-[[3-[3-fluoro-4-(4-morpholinyl) phenyl]-2-oxo-5-oxazolidinyl] methyl]-acetamide. The empirical formula of linezolid is C16H20FN3O4 and the molecular weight of 337.35.