SUMMARY CMI
BTC Candesartan
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI) summary
The full CMI on the next page has more details. If you are worried about using this medicine, speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
1. Why am I using BTC Candesartan?
BTC Candesartan contains the active ingredient candesartan cilexetil. BTC Candesartan is used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure (in combination with other medicines to treat your condition).
For more information, see Section 1. Why am I using BTC Candesartan? in the full CMI.
2. What should I know before I use BTC Candesartan?
Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to BTC Candesartan or any of the ingredients listed at the end of the CMI. Talk to your doctor if you have any other medical conditions, take any other medicines, or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding.
For more information, see Section 2. What should I know before I use BTC Candesartan? in the full CMI.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Some medicines may interfere with BTC Candesartan and affect how it works.
A list of these medicines is in Section 3. What if I am taking other medicines? in the full CMI.
4. How do I use BTC Candesartan?
- Your doctor will tell you how many tablets to take each day. The usual dose is 8 mg or 16 mg once daily. This dose may be increased to 32 mg once daily.
- Swallow the tablets whole with a glass of water at about the same time each day
More instructions can be found in Section 4. How do I use BTC Candesartan? in the full CMI.
5. What should I know while using BTC Candesartan?
| Things you should do |
|
| Things you should not do |
|
| Driving or using machines |
|
| Drinking alcohol |
|
| Looking after your medicine |
|
For more information, see Section 5. What should I know while using BTC Candesartan? in the full CMI.
6. Are there any side effects?
Common side effects: headache, chest or throat infection, flu-like symptoms, feeling sick (nausea, vomiting), back pain or dizziness.
Serious side effects: swelling of the face, lips, tongue or throat which may cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing; swelling of the hands, feet or ankles; aching muscles, tenderness of weakness in the muscles, worsening of the kidney function including passing little or no urine, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, breathlessness, loss of appetite and weakness (especially in patients with existing kidney problems or heart failure).
For more information, including what to do if you have any side effects, see Section 6. Are there any side effects? in the full CMI.
FULL CMI
BTC Candesartan
Active ingredient(s): Candesartan cilexetil
Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
This leaflet provides important information about using BTC Candesartan. You should also speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you would like further information or if you have any concerns or questions about using BTC Candesartan.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
1. Why am I using BTC Candesartan?
2. What should I know before I use BTC Candesartan?
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
4. How do I use BTC Candesartan?
5. What should I know while using BTC Candesartan?
6. Are there any side effects?
7. Product details
1. Why am I using BTC Candesartan?
BTC Candesartan contains the active ingredient candesartan cilexetil.
BTC Candesartan belongs to a group of medicines called angiotensin II receptor antagonists (or blocker).
BTC Candesartan is used to treat
- high blood pressure, also called hypertension.
- heart failure, in combination with other medicines to treat your condition.
2. What should I know before I use BTC Candesartan?
Warnings
Do not use BTC Candesartan if:
- you are allergic to candesartan cilexetil, any medicine containing an angiotensin II receptor antagonist (blocker) or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet. Always check the ingredients to make sure you can use this medicine.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include:
- shortness of breath
- wheezing or difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body
- rash, itching or hives on the skin. - you have severe liver disease and/or conditions associated with impaired bile flow (cholestasis)
- you are taking blood pressure medicine containing aliskiren, especially if you have diabetes mellitus or have kidney problems.
Check with your doctor if you:
- have any other medical conditions
- kidney problems
- liver problems
- heart problems
- recent excessive vomiting or diarrhoea
- a condition called primary hyperaldosteronism. - take medicines for any other condition
- During treatment, you may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It is important you understand these risks and how to monitor for them. See additional information under Section 6. Are there any side effects?
Use in Children
BTC Candesartan should not be given to children. There is not enough information to recommend the use of this medicine for children.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Do not take BTC Candesartan if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
It may affect your developing baby if you take it during pregnancy.
Do not breastfeed if you are taking this medicine.
Talk to your doctor if you intend to breastfeed. It is not known if this medicine passes into breast milk.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any medicines, vitamins, or supplements that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy, supermarket, or health food shop.
Some medicines may interfere with BTC Candesartan and affect how it works. These include:
- any medicines containing potassium, including salt substitutes
- diuretics (fluid tablets)
- lithium, a medicine used to treat mood swings and some types of depression
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), medicines used to relieve pain, swelling and other symptoms of inflammation, including arthritis.
- Angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, medicines used to help lower blood pressure, especially if you have diabetes related kidney problems
- Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs), such as spironolactone and eplerenone, medicines used to treat heart failure.
Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines, vitamins, or supplements you are taking and if these affect BTC Candesartan.
4. How do I use BTC Candesartan?
How much to take
- The usual dose is 8 or 16 mg taken once daily. Sometimes an increase in dose to 32 mg once daily is needed.
- Follow the instructions your doctor or pharmacist give you. If you take the wrong dose, BTC Candesartan may not work as well, and your problem may not improve.
When to take BTC Candesartan
- BTC Candesartan should be taken once a day, at about the same time each day. Taking it at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will also help you remember when to take it
How to take BTC Candesartan
Swallow the tablets whole with a full glass of water. It does not matter whether you take this medicine with food or on an empty stomach.
How to long to take BTC Candesartan
Continue taking BTC Candesartan for as long as your doctor tells you. This medicine helps to control your condition but does not cure it. It is important to keep taking your medicine even if you feel well.
If you forget to use BTC Candesartan
If you miss your dose at the usual time, take it as soon as you remember (as long as it is at least 12 hours before your next dose is due), and continue to take it as you would normally.
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next dose when you are meant to.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose you missed. This may increase the chance of you getting an unwanted side effect.
If you are not sure what to do, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have trouble remembering to take your medicine, ask your pharmacist for some hints.
If you use too much BTC Candesartan
If you think that you have used too much BTC Candesartan, you may need urgent medical attention.
You should immediately:
- phone the Poisons Information Centre
(by calling 13 11 26), or - contact your doctor, or
- go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
Symptoms of overdose may include a headache, feel sick (nausea), dizziness or tiredness.
5. What should I know while using BTC Candesartan?
Things you should do
- Take BTC Candesartan exactly as your doctor has told you to. Your blood pressure will not be well controlled if you do not.
- If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor or pharmacist that you are taking BTC Candesartan
- If you are going to have surgery (even at the dentist) that needs a general anaesthetic, tell the surgeon or anaesthetist that you are taking this medicine.
- Be sure to keep all of your doctor's appointments so that your progress can be checked. Your doctor will check your progress and may want to take some test (e.g., blood tests, blood pressure) from time to time. These tests may help to prevent side effects.
Call your doctor straight away if you:
- become pregnant while taking this medicine. You should not take this medicine if you are pregnant or thinking about becoming pregnant. Your doctor can discuss different treatment options with you.
Remind any doctor, dentist, or pharmacist you visit that you are using BTC Candesartan.
Things you should not do
- Do not take BTC Candesartan to treat any other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
- Do not give your medicine to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
- Do not stop taking your medicine or lower the dosage without checking with your doctor.
Things to be careful of
- Move slowly when getting out of bed or standing up if you feel faint, dizzy, or light-headed.
- If you are taking this medicine for high blood pressure, drink plenty of water during exercise and hot weather, especially if you sweat a lot.
- If you do not drink enough water while taking this medicine, you may faint or feel light-headed or sick. This is because your body doesn't have enough fluid and your blood pressure is low. If you continue to feel unwell, tell your doctor.
- If you are taking this medicine for heart failure, restricted fluid intake is generally recommended. Speak with your doctor about how much water you should drink.
Driving or using machines
Be careful before you drive or use any machines or tools until you know how BTC Candesartan affects you. This medicine may cause nausea, dizziness, and tiredness in some people. If you have any of these symptoms, do not drive, operate machinery, or do anything else that could be dangerous.
Drinking alcohol
Tell your doctor if you drink alcohol.
Looking after your medicine
- Keep BTC Candesartan in the original container.
Follow the instructions in the carton on how to take care of your medicine properly.
Store it in a cool dry place below 30°C away from moisture, heat, or sunlight; for example, do not store it:
- in the bathroom or near a sink, or
- in the car or on window sills.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it.
A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place to store medicines.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date, take it to any pharmacy for safe disposal.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date or if the packaging is torn or shows signs of tampering.
6. Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. If you do experience any side effects, most of them are minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any further questions about side effects.
Less serious side effects
| Less serious side effects | What to do |
Infection related:
| Speak to your doctor if you have any of these less serious side effects and they worry you. They are generally mild and do not cause patients to stop taking BTC Candesartan. |
Serious side effects
| Serious side effects | What to do |
Allergy related:
| Call your doctor straight away or go straight to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects. |
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that may be making you feel unwell.
Other side effects not listed here may occur in some people.
Reporting side effects
After you have received medical advice for any side effects you experience, you can report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration online at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you decide to stop taking any of your medicines.
7. Product details
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What BTC Candesartan contains
| Active ingredient (main ingredient) | candesartan cilexetil |
| Other ingredients (inactive ingredients) |
|
| Potential allergens |
This medicine does not contain sucrose, gluten, tartrazine, or any other azo dyes. |
Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of these ingredients.
What BTC Candesartan looks like
BTC Candesartan 4 mg - white, round biconvex tablet, debossed with 4 on one side and scored on the other side (AUST R 396088).
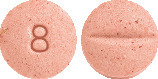
BTC Candesartan 8 mg - pink, mottled, round biconvex tablet, debossed with 8 on one side and scored on the other side (AUST R 396085).
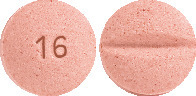
BTC Candesartan 16 mg - pink, mottled, round biconvex tablet, debossed with 16 on one side and scored on the other side (AUST R 396089).
BTC Candesartan 32 mg - pink, mottled, round biconvex tablet, debossed with 32 on one side and scored on the other side (AUST R 396087).
Available in blisters of 30 tablets.
Who distributes BTC Candesartan
Sandoz Pty Ltd
ABN 60 075 449 553
54 Waterloo Road
Macquarie Park, NSW 2113
Tel: 1800 726 369
This leaflet was prepared in January 2023.
Published by MIMS July 2023




 The antihypertensive effects of candesartan cilexetil and losartan potassium at their highest recommended doses administered once daily were compared in two randomised, double blind trials. In a total of 1,268 patients with mild to moderate hypertension who were not receiving other antihypertensive therapy, candesartan cilexetil 32 mg lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure by 2 to 3 mmHg on average more than losartan potassium 100 mg, when measured at the time of either peak or trough effect.
The antihypertensive effects of candesartan cilexetil and losartan potassium at their highest recommended doses administered once daily were compared in two randomised, double blind trials. In a total of 1,268 patients with mild to moderate hypertension who were not receiving other antihypertensive therapy, candesartan cilexetil 32 mg lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure by 2 to 3 mmHg on average more than losartan potassium 100 mg, when measured at the time of either peak or trough effect.

 All-cause mortality was also assessed in pooled populations, CHARM-Alternative and CHARM-Added (HR 0.88, 95% CI: 0.79 to 0.98, p = 0.018) and all three studies (HR 0.91, 95% CI: 0.83 to 1.00, p = 0.055). This corresponds to a relative risk reduction of 12 and 9% respectively and an absolute risk reduction of 2.9 and 1.6% respectively.
All-cause mortality was also assessed in pooled populations, CHARM-Alternative and CHARM-Added (HR 0.88, 95% CI: 0.79 to 0.98, p = 0.018) and all three studies (HR 0.91, 95% CI: 0.83 to 1.00, p = 0.055). This corresponds to a relative risk reduction of 12 and 9% respectively and an absolute risk reduction of 2.9 and 1.6% respectively.
